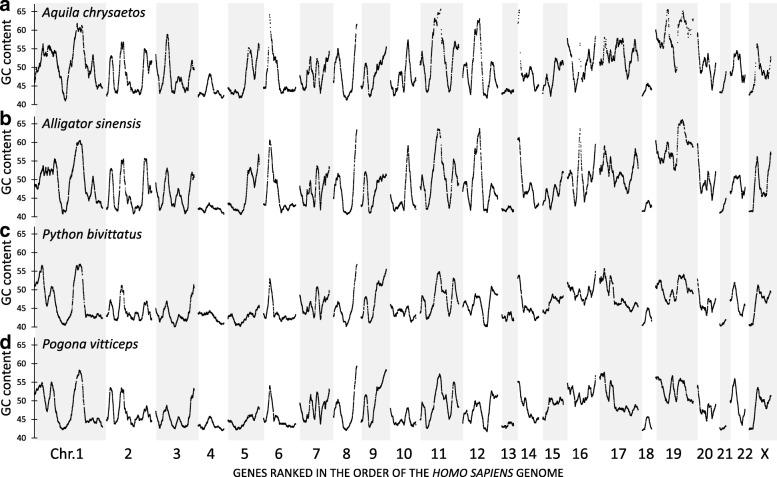
Fig. 2.
Genome-wide landscapes of base composition of predicted mRNAs from four reptiles. a. Aquila chrysaetos canadensis (golden eagle), b. Alligator sinensis (Chinese alligator), c. Python bivittatus (Burmese python), and d. Pogona vitticeps (central bearded dragon). Genes were ranked on the order of the human genome and GC content was calculated using a sliding window approach of a gene and its 100 surrounding genes. Only minor differences between the landscapes of these four reptiles can be observed, while major differences can be seen compared to the mammalian landscapes of Fig. 1