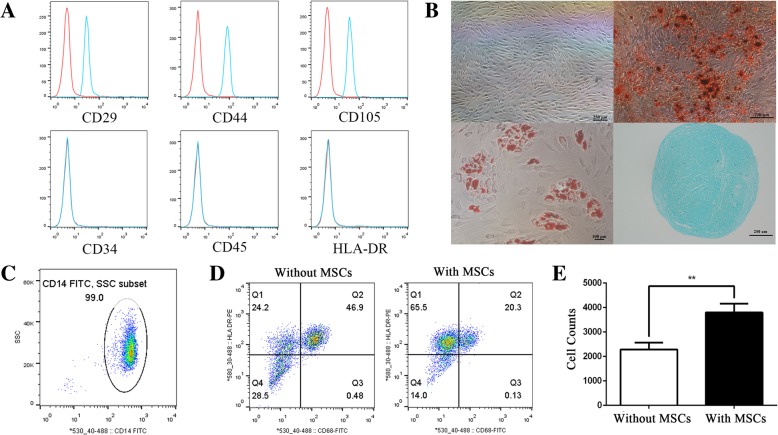
Fig. 1.
MSCs and their regulatory function in CD14+ monocytes. a Cell markers of MSCs were analysed by flow cytometry. MSCs were negative for CD45, CD34 and HLA-DR and positive for CD29, CD105 and CD44. b Alizarin red S staining (× 40), ALP staining (× 40), oil red staining (× 100) and toluidine blue staining (× 40) were used to detect MSC differentiation. c Flow cytometric analysis of the purity of CD14+ monocytes. d The differentiation ratio of M1 macrophages (CD68 and HLA-DR positive) was decreased upon co-culture with MSCs. e MSCs promote monocyte migration, as detected by flow cytometry. Introduction of the RNA-seq experiments: MSCs and CD14+ monocytes were separately isolated. lncRNAs and mRNAs that were DE between the control group (MSCs only) and co-culture group (MSCs co-cultured with monocytes) were identified through high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatic analyses and confirmed by qRT-PCR. Bioinformatic analyses were performed to identify key biological functions and signalling pathways involved in MSC-mediated monocyte regulation. Additionally, functional networks were constructed from the DE mRNAs and lncRNAs