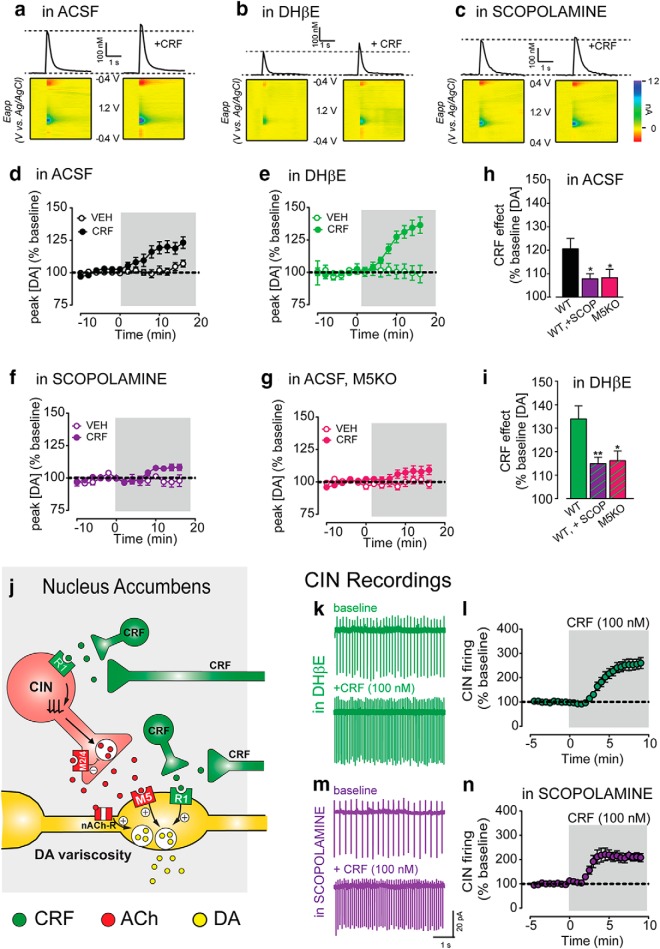
Figure 7.
CRF potentiation of DA transmission requires mACh-R type 5 receptor activation. a, Representative current-time traces and corresponding 3-D color plots of electrically evoked dopamine transients before and following CRF application in slices maintained in ACSF (a), ACSF +DHβE (1 μm; b), ACSF +Scopolamine (1 μm; c). d, Mean time course of electrically evoked DA transients recorded before or after CRF or vehicle application in WT control NAc slices incubated and maintained in ACSF. e, Mean time course of electrically evoked DA transients recorded before or after CRF or vehicle application in WT control (in-house C57Bl/6J) NAc slices incubated and maintained in ACSF + DHβE. f, Mean time course of electrically evoked DA transients recorded before or after CRF or vehicle application in WT control NAc slices incubated and maintained in ACSF + Scopolamine. g, Mean time course of electrically evoked DA transients recorded before or after CRF or vehicle application in M5KO NAc slices incubated and maintained in ACSF. h, Average maximal CRF effect on peak [DA] (% baseline) in experiments conducted in ACSF. i, Average maximal CRF effect on peak [DA] (% baseline) in experiments conducted in ACSF + DHβE. j, Schematic of CRF function in the NAc under normal conditions. k, l, Representative traces (k) and normalized time course (l) of NAc CINs before and following CRF application in slices incubated and maintained DHβE. m, n, Representative traces (m) and normalized time course (n) of NAc CINs before and following CRF application in slices incubated and maintained scopolamine. Asterisks denote statistical significance p < 0.05 (*) and p < 0.01 (**).