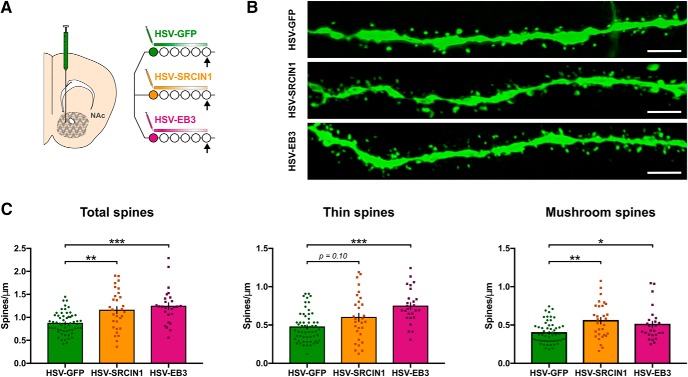
Figure 5.
EB3 and SRCIN1 overexpression in the NAc both increase spine density and modulate dendritic spine morphology. A, Experimental time line for spine morphology analysis. Mice were injected in the NAc with an HSV overexpressing EB3 (n = 26 neurites across 3 mice), SRCIN1 (n = 30 neurites across 3 mice), or a control GFP vector (n = 57 neurites across 6 mice), and were perfused for immunostaining after 5 d. B, Representative confocal images of HSV-infected neurites. Scale bar, 5 μm. C, Both HSV-SRCIN1 and HSV-EB3 viruses increased the total number of spines (Kruskal–Wallis test: H(2) = 22.53, p < 0.0001; followed by Dunn's post hoc testing: HSV-SRCIN1, p = 0.021; HSV-EB3, p < 0.0001 vs HSV-GFP), affecting both thin (Kruskal–Wallis test: H(2) = 20.46, p < 0.0001; followed by Dunn's post hoc testing: HSV-SRCIN1, p = 0.1016; HSV-EB3, p < 0.0001 vs HSV-GFP) and mushroom spines (Kruskal–Wallis test: H(2) = 12.78, p = 0.0017; followed by Dunn's post hoc testing: HSV-SRCIN1, p = 0.0016; HSV-EB3, p = 0.0465 vs HSV-GFP). Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for post hoc tests.