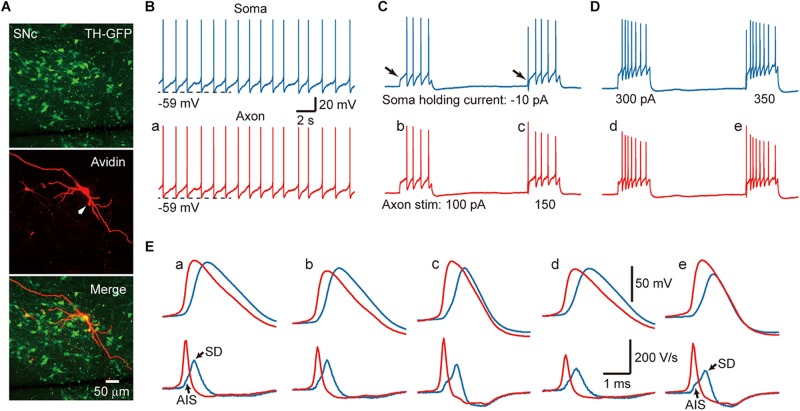
FIGURE 1.
Action potentials (APs) are initiated at the AIS of SNc TH-positive neurons. (A) An example recorded SNc TH-GFP neuron. (B) Dual whole-cell recording from the soma (blue) and the axon (red, 10 μm away from the soma) showing pace making activity at both recording sites. (C) Negative DC current injection to the soma prevents spontaneous firing. Positive current pulses (500 ms in duration) at the AIS cause repetitive firing at the axon and the soma. Note the absence and presence of the initial AP (arrows) in response to weak and strong current pulses (100 vs. 150 pA). (D) Injection of current pulses to the soma evoke repetitive firing at both recording sites. Also note the absence of presence of the initial AP. (E) Top, expansion of the APs indicated in B–D. Axonal APs precede the somatic APs in all cases. Bottom, the first derivative (dV/dt) of the corresponding APs. The two components at the rising phase of the somatic dV/dt trajectory (blue) correspond to the AIS and SD potentials, respectively. Note the difference of the rising phase between somatic and axonal dV/dt traces.