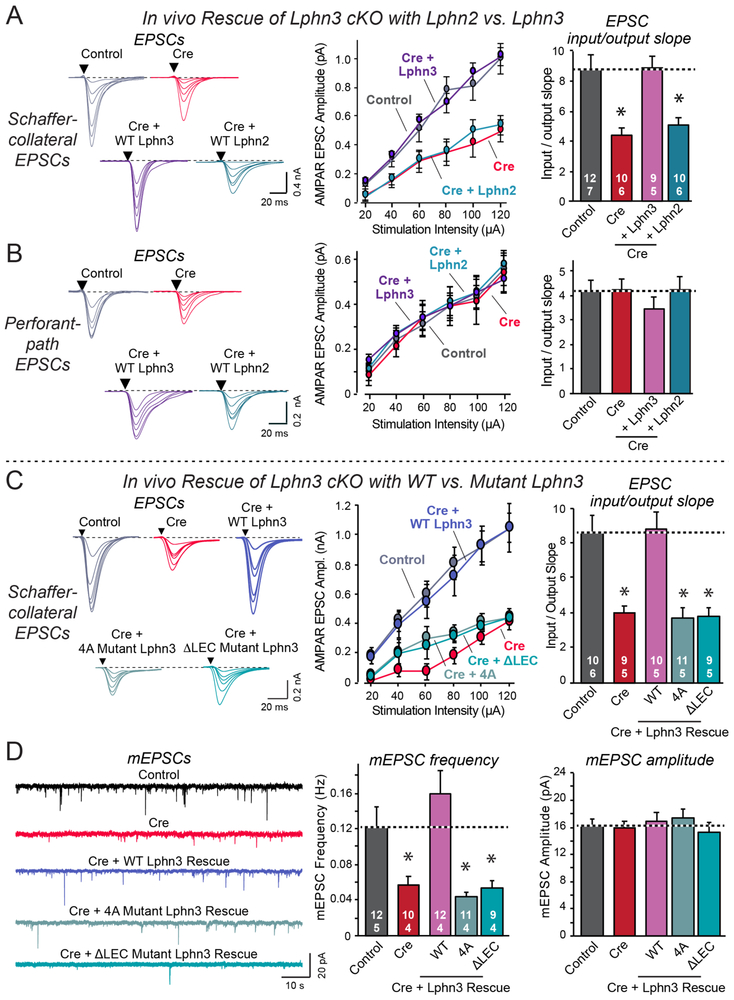
Figure 5: Neither wild-type Lphn2 nor mutant Lphn3 lacking FLRT- or teneurin-binding activity rescue the decrease in Schaffer-collateral synaptic strength induced by Lphn3 deletion.
Experiments were performed by whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from CA1 neurons in acute slices from Lphn3 cKO mice that were lentivirally-infected at P0 as described in Figure 4A and 4F.
A & B. Wild-type Lphn3 but not wild-type Lphn2 fully rescues the decrease in Schaffer-collateral synaptic strength induced by loss of Lphn3 (A), while none of the manipulations affects entorhinal cortex-derived synapses (B).
C. Although wild-type Lphn3 fully rescues the decrease in Schaffer-collateral synaptic strength induced by Lphn3 deletion, mutant Lphn3 lacking FLRT-binding (4A) or teneurin-binding (ΔLEC) was unable to rescue.
D. Wild-type Lphn3 also fully rescues the decrease in mEPSC frequency induced by Lphn3 deletion, but again mutant Lphn3 lacking FLRT-binding (4A) or teneurin-binding (ΔLEC) was unable to rescue, with none of the manipulations having any effect on mEPSC amplitude.
Numerical data are means ± SEM (numbers of cells/experiments are indicated in bars). Statistical significance was assessed by one-way ANOVA (* denotes p<0.05).