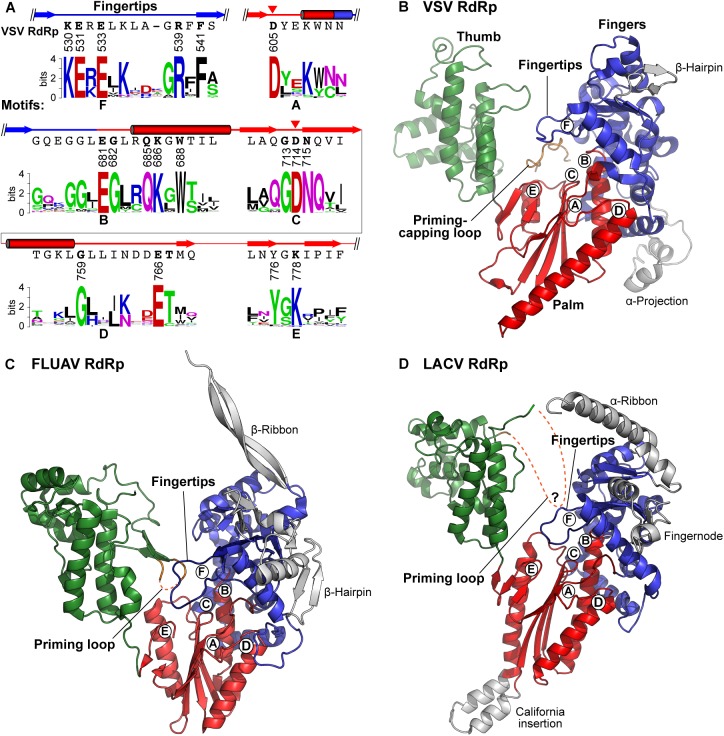
FIGURE 6.
Structures of negative strand RNA viral RdRp domains. (A) Partial amino acid sequences containing RdRp motifs A–F of the VSV L protein are shown with their secondary structures (cylinders, α-helices; arrows, β-strands). The catalytic aspartate residues are indicated by red arrowheads. Amino acid sequence logos for RdRp motifs A–F in L proteins of 231 NNS RNA viruses belonging to the Rhabdoviridae, Paramyxoviridae, Filoviridae, Bornaviridae, and Nyamiviridae families (Maes et al., 2019) were generated using the WebLogo program (Crooks et al., 2004)2 as described in Neubauer et al. (2016). (B–D) The three-dimensional structural model of the RdRp domain of VSV (B) is compared with those of influenza A virus [FLUAV, PDB id: 4WSB (Pflug et al., 2014)] (C), and LACV [PDB id: 5AMQ (Gerlach et al., 2015)] (D). Their fingers, palm, and thumb subdomains are colored as in Figure 5A. The positions of RdRp motifs A–F are indicated by circled letters. The priming-capping loop of the VSV PRNTase domain and priming loops extended from the C-terminal regions of the FLUAV and LACV thumb subdomains are shown in orange. Missing regions of the loops in the structures are denoted by orange dashed lines. Other virus-specific substructures in their fingers subdomains are colored gray.