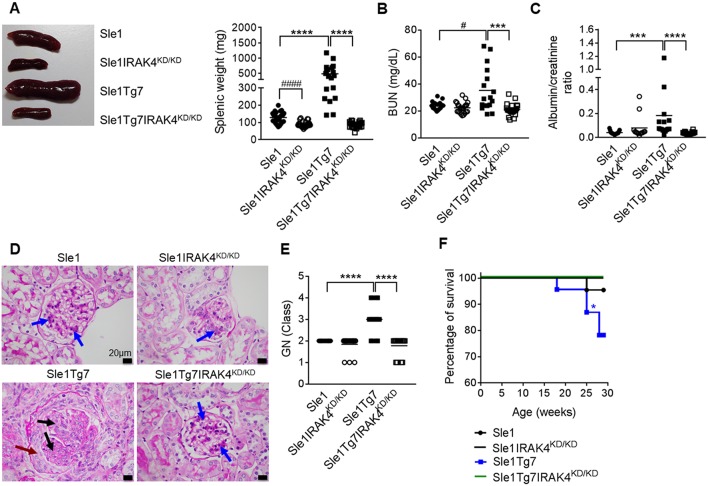
Figure 1.
Prevention of spleen and kidney disease with the elimination of IRAK4 kinase activity. Sle1, Sle1IRAK4KD/KD, Sle1Tg7, and Sle1Tg7IRAK4KD/KD female mice were aged to 6–7 months and analyzed for lupus disease parameters. (A) Photograph showing representative spleens from indicated strains and cumulative splenic weight (19–27 mice/group). Functional kidney assessment using (B) a blood urea nitrogen (BUN) assay in the same mice (17–23 mice/group) and (C) urine albumin levels normalized to creatinine (13–18 mice per group). Assessment of kidney disease class by PAS stain with (D) representative photomicrographs (original magnification x600, Black bars represent 20 μm), showing glomerular segments with mild mesangial proliferation (blue arrows), glomerular segments with endocapillary proliferation (black arrows) and cellular crescent (maroon arrow). (E) Cumulative data for kidney GN class for 17–19 mice/group (class I–IV represented as numbers 1–4). Parametric data were assessed by 1-way ANOVA (with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test) and non-parametric data with Kruskal-Wallis (with Dunn's multiple comparisons test) ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Additional comparisons between two groups were made with a Student's t test or Mann-Whitney test for parametric and non-parametric data, respectively, indicated by # (#P < 0.05, ####P < 0.0001). (F) Survival curves for each strain (22–23 mice per group); Sle1Tg7 mice survive significantly less than Sle1Tg7IRAK4KD/KD (*P < 0.05, Mantel-Cox test).