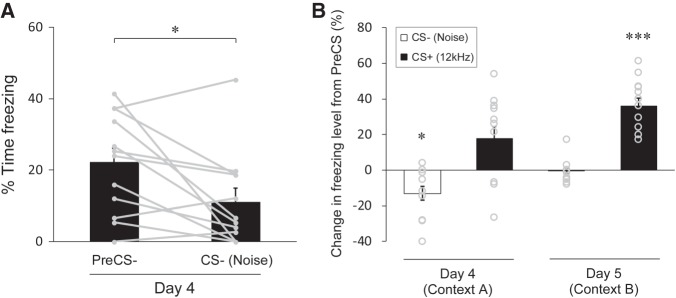
Figure 4.
Discriminative safety and fear learning in a paradigm with the tone CS+ and the noise CS−. (A) Percent time spent freezing in trials with the noise CS− in the testing session with the conditioning context (day 4). The freezing level is significantly lower during the CS− than during the PreCS−, indicating inhibition of contextual fear is caused by the noise CS−. (B) Changes in freezing levels represented as the percent time spent freezing during the CS subtracted by that during the corresponding PreCS of the trial. Opposite changes in freezing levels between the CS− on day 4 (decrease) and the CS+ on day 5 (increase) indicate safety specific for the noise CS− and fear specific for the tone CS+. Gray dots with lines (A) and circles (B) represent the median of data sets from three trials for individual mice (n = 12 mice). All data in bar graphs are depicted as mean ± SEM. (*) P < 0.05, (***) P < 0.001. P values were obtained using a two-tailed paired t-test (A) and a one-tailed paired t-test (B).