Figure 1.
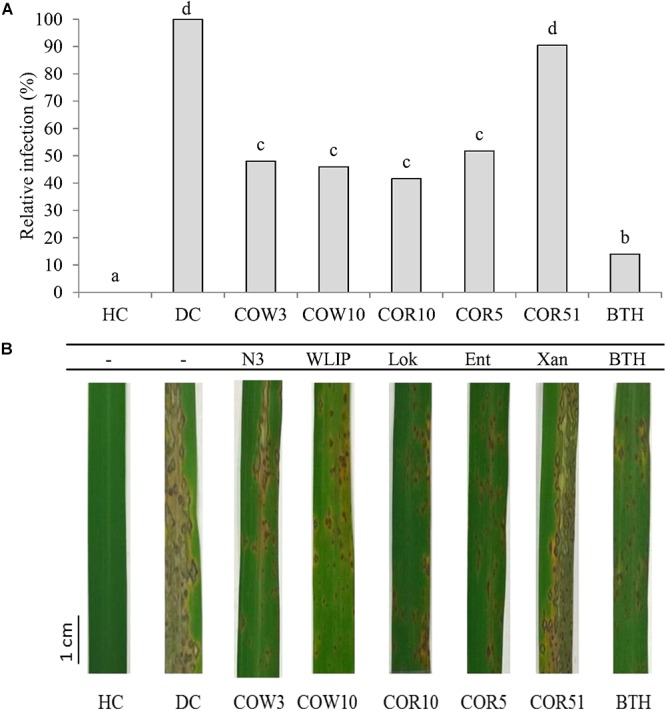
Induced systemic resistance (ISR) capacity of CLP-producing Pseudomonas spp. to M. oryzae in rice. (A) The potential of root application with Pseudomonas sp. strains COW3 (N3), COW10 (WLIP), COR10 (lokisin), COR5 (entolysin) and COR51 (xantholysin) to induce systemic resistance (ISR) against M. oryzae isolate VT5M1 on rice. HC: healthy control and DC: disease control plants were treated with water. Data of one experiment made up of three biological replicates, each consisting of twelve (12) plants are shown. The experiment was repeated with similar results. Different letters indicated statistically significant differences among different treatments (ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s tests: n = 36; α = 0.05), Lok, lokisin; Ent, entolysin; Xan, xantholysin; BTH, S-methyl 1,2,3-benzothiadiazole-7-carbothioate. (B) Representative pictures of disease symptoms observed on the second youngest leaf after 6 days post-inoculation with M. oryzae. Scale bar represents 1 cm.
