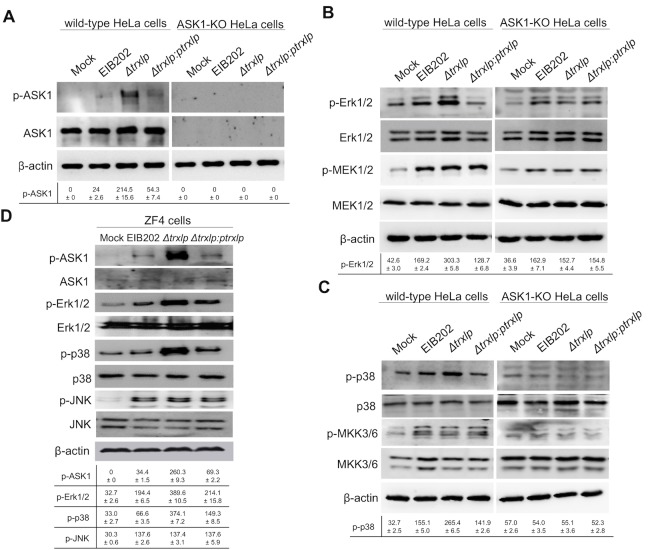
Fig 4. Trxlp suppresses the phosphorylation of Erk1/2 and p38 dependent on ASK1 during E. piscicida infection.
(A-C) Immunoblotting assays of ASK1, MAP2Ks and MAPKs activation during E. piscicida infection in HeLa cells. Wild-type HeLa cells and ASK1-KO HeLa cells were infected with EIB202, Δtrxlp, or trxlp-complemented E. piscicida at a MOI of 100 for 2 h. Cell lysates were collected and probed for anti-phospho-ASK1 and anti-ASK1 antibodies (A), or probed for anti-phospho-Erk1/2 and anti-Erk1/2, and anti-phospho-MEK1/2 and MEK1/2 antibodies (B), or probed for anti-phospho-p38α and anti-p38α, and anti-phospho-MKK3/6 and MKK3/6 antibodies (C). (D) Immunoblotting assays of ASK1 and MAPKs activation during E. piscicida infection in Zebrafish fibroblasts (ZF4). ZF4 cells were infected with EIB202, Δtrxlp, or trxlp-complemented E. piscicida for 2 h at a MOI of 10. Cell lysates were probed with anti-phospho-ASK1 and anti-ASK1, anti-phospho-Erk1/2 and anti-Erk1/2, anti-phospho-p38 and anti-p38, anti-phospho-JNK and anti-JNK antibodies. (A-D) β-Actin is shown as a loading control. The signal intensities were quantitatively analyzed using Quantity one software. Data (Means ± SD) are representative of at least 3 experiments.