Figure 7. Inhibition of IL-1α Protects WT Mice from Tumor Induction.
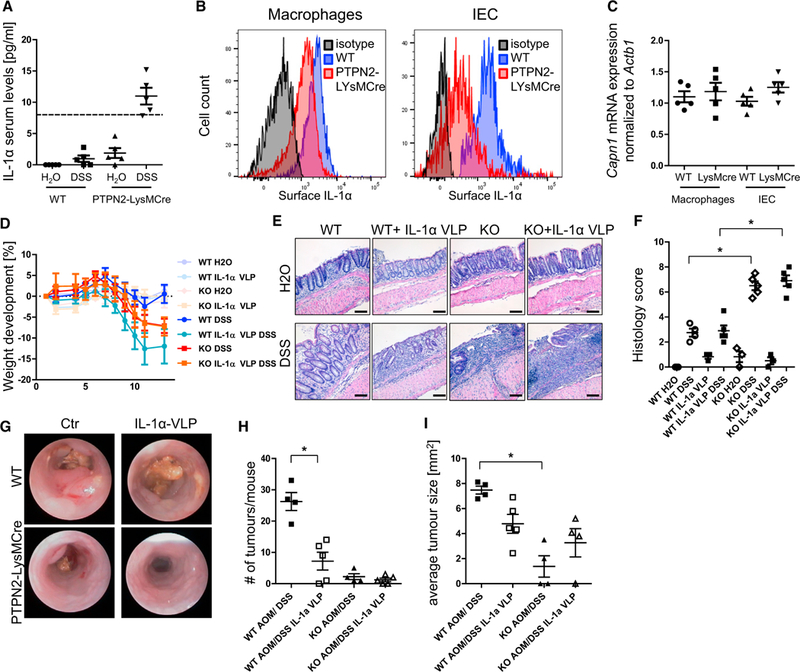
(A) Serum from WT and PTPN92-LysMCre mice with chronic DSS colitis was analyzed for IL-1α levels. Dashed line, detection limit of the ELISA.
(B and C) Peritoneal macrophages and intestinal epithelial cells (lECs) from WT and PTPN2-LysMCre mice were analyzed for IL1a surface expression (B) and calpain mRNA levels (C).
(D–F) WT and PTPN2-LysMCre mice were immunized with IL-1α-coupled Qβ virus-like particles (IL-1α VLP) or with control Qβ virus-like particles 5,3, and 1 week prior to start of colitis and/or tumor induction. (D) Weight development of mice in acute colitis, (E) representative pictures of H&E-stained slides, and
(F) quantification of histology score of terminal colon pieces from WT and PTPN2-LysMCre mice subjected to chronic colitis.
(G-I) Representative pictures of colonoscopy (G), observed tumor number in dissected colon (H), and average tumor size (I) in each mouse in the AOM/DSS tumor model.
Results are representative of one of two independent experiments with three to five mice per group. Asterisks denote statistical significance (*p < 0.05; MannWhitney U test with Bonferroni correction). Scale bars represent 100 mm. Error bars represent means ± SD.
