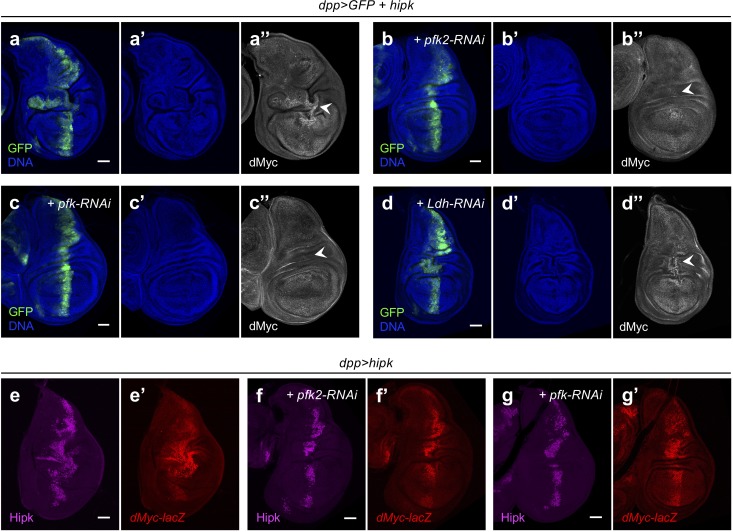
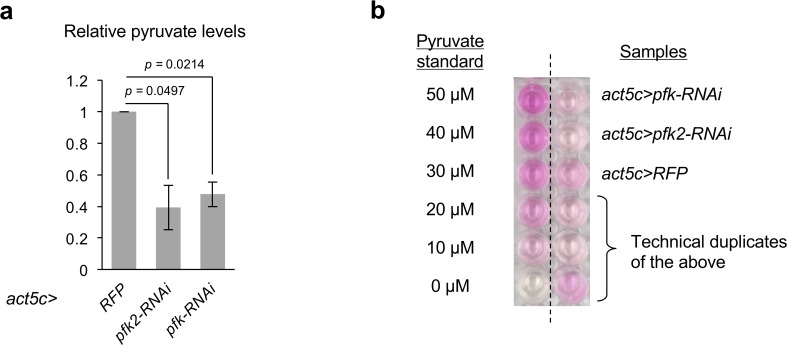
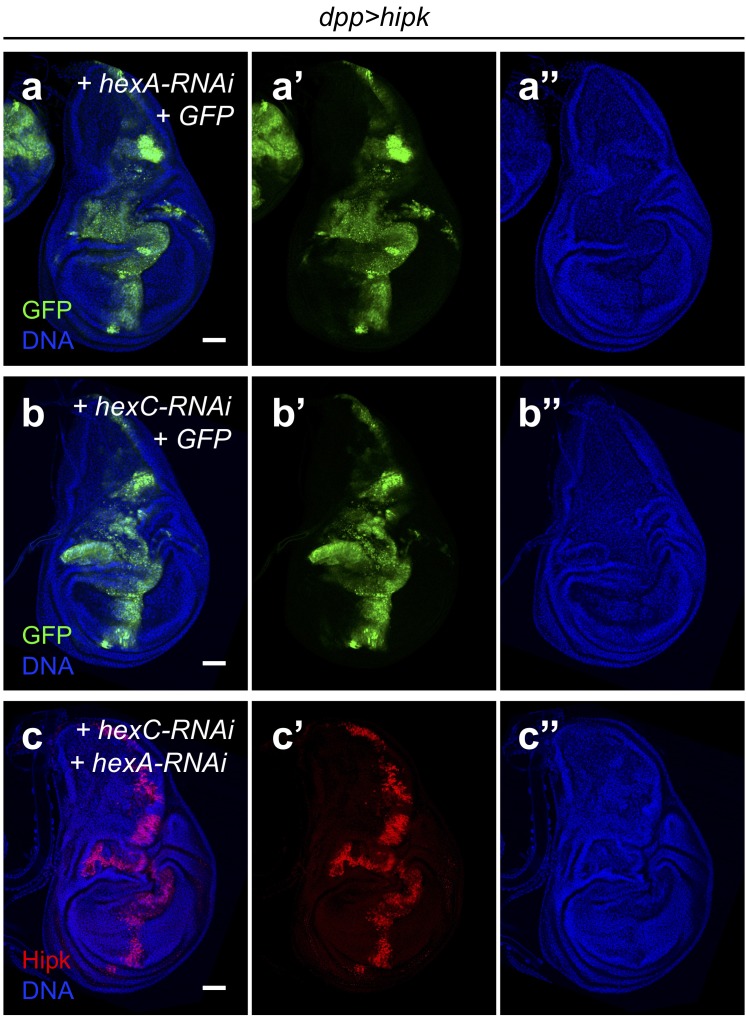
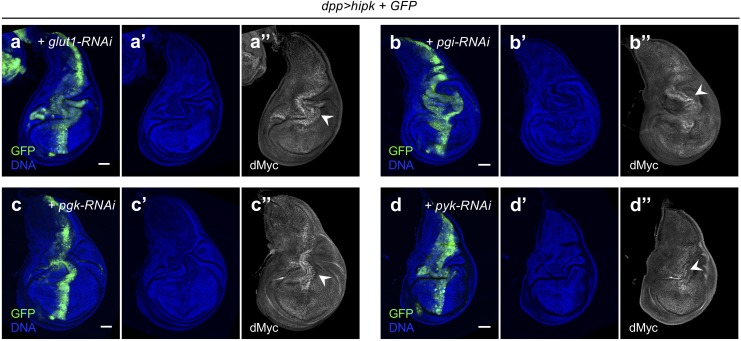
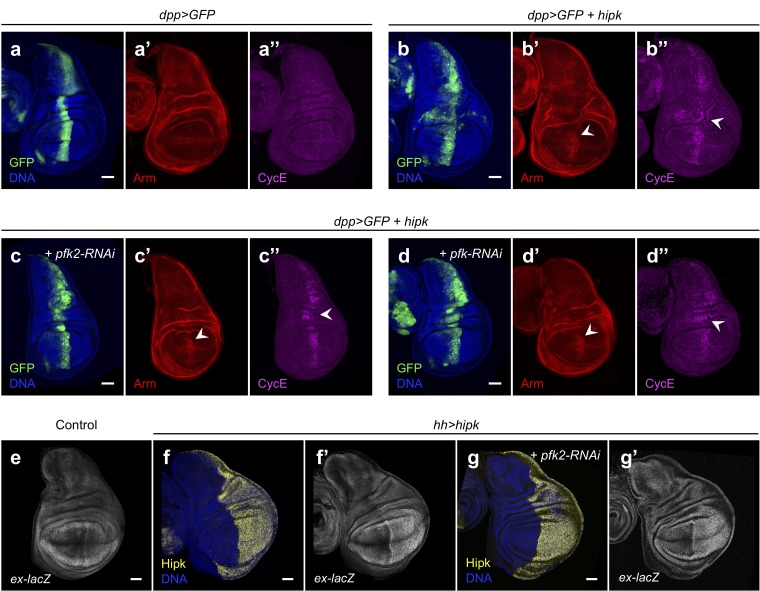
Figure 6. Pfk2 and Pfk sustain Hipk tumor growth through post-transcriptional regulation of dMyc.
(a–d) dMyc staining (gray in a’’, b’’, c’’ and d’’) in hipk-expressing wing disc (dpp>GFP + hipk) (a), hipk and pfk2-RNAi co-expressing disc (dpp>GFP + hipk + pfk2-RNAi) (b), hipk and pfk-RNAi co-expressing disc (dpp>GFP + hipk + pfk-RNAi) (c) and hipk and Ldh-RNAi co-expressing disc (dpp>GFP + hipk + Ldh-RNAi) (d). GFP (green) marks the transgene-expressing cells. DAPI staining for DNA (blue) reveals tissue morphology. (e–g) Hipk staining (magenta in e, f and g) and β-galactosidase staining (red in e’, f’ and g’) in hipk-expressing disc (dpp>hipk) (e), hipk and pfk2-RNAi co-expressing disc (dpp>hipk + pfk2-RNAi) (f), hipk and pfk-RNAi co-expressing disc (dpp>hipk + pfk-RNAi) (g). All wing discs harbor a lacZ reporter to monitor the transcriptional induction of dMyc (dMyc-lacZ). Scale bars, 50 μm.