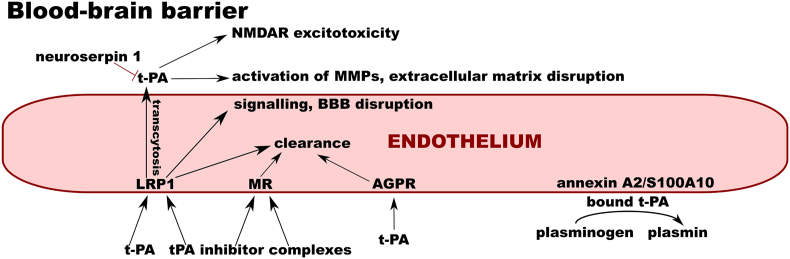
Fig. 4.
Interactions of t-PA on the blood-brain barrier. On the endothelial cell surface, tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) binds annexin A2/S100A10. This leads to plasminogen activation on the cell surface. The free form, as well as inhibitor complexes of t-PA, are endocytosed by asialoglycoprotein receptor (AGPR), mannose receptor (MR), and low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), leading to their clearance. T-PA can cross the intact blood-brain barrier (BBB) via LRP1-dependent transcytosis. In the brain parenchyma, it can activate matrix metalloproteinases and interact with the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). These effects are inhibited by neuroserpin 1, the inhibitor of tPA in the brain parenchyma.