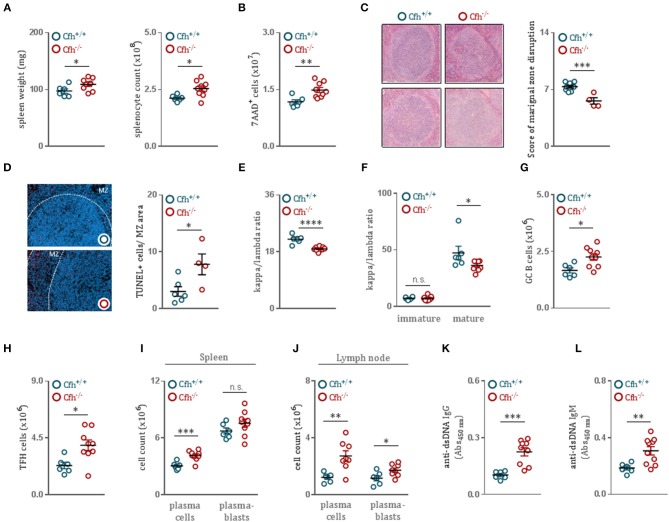
Figure 4.
CFH deficient mice develop germinal center hyperactivity with robust autoantibody titers. (A) Spleen weight and absolute splenocyte count of 8 month-old Cfh+/+ (blue dots) and Cfh−/− (red dots) mice. (B) Total numbers of 7AAD+ dying splenocytes of Cfh+/+ (blue dots) and Cfh−/− (red dots) mice, measured by flow cytometry. (C) Representative images demonstrating the white pulp architecture of 8 month-old Cfh+/+ and Cfh−/− mice. Dot plots show the score of marginal zone disruption in the spleens of Cfh+/+ (blue dots) and Cfh−/− (red dots) mice. (D) Representative images showing TUNEL staining of spleen sections from 8 month-old Cfh+/+ and Cfh−/− mice. Dot plots indicate the average numbers of TUNEL+ cells in the marginal zone area in the spleens of Cfh+/+ (blue dots) and Cfh−/− (red dots) mice. Dot plots represent the kappa/lambda light chain ratio of (E) IgD+CD19+CD43− mature splenic B cells as well as (F) B220hiCD23+CD43− mature and B220loCD23−CD43− immature splenic B cells of Cfh+/+ (blue dots) and Cfh−/− (red dots) mice assessed by flow cytometry. Absolute numbers of (G) GL-7+B220+ germinal center B cells and (H) CD3+CD4+CXCR5+PD-1+ follicular helper T cells in the spleen of Cfh+/+ (blue dots) and Cfh−/− (red dots) mice quantified by flow cytometry. (I,J) Quantification of CD138+B220− plasma cells and CD138+B220+ plasmablasts in the spleen as well as in the lymph node of Cfh+/+ (blue dots) and Cfh−/− (red dots) mice by flow cytometry. (K) IgG and (L) IgM titers specific for double stranded-DNA in the plasma of aged Cfh+/+ (blue dots) and Cfh−/− (red dots) mice determined by ELISA. All results show mean ± SEM, each symbol represents an individual mouse, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 (unpaired t-test).