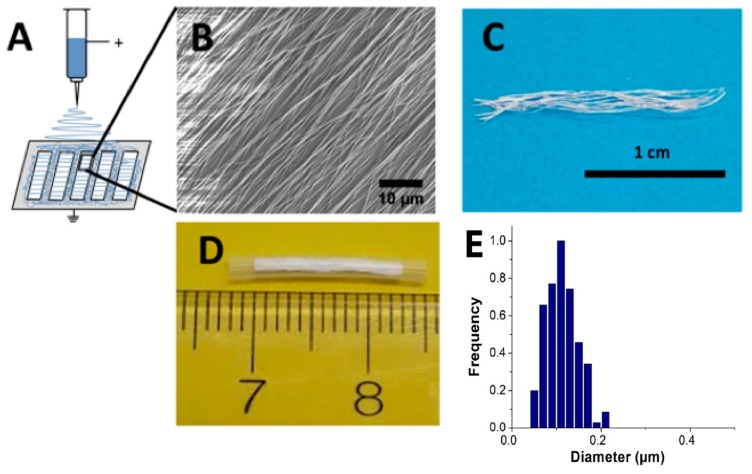
Figure 1.
(A) Electrospinning setup for aligned nanofibers: a solution of 4-dibenzocyclooctynol (DIBO)-terminated poly(ɛ-caprolactone) in 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol (HFIP, 17% w/v) was placed in a syringe, and a voltage of 15 kV was applied to form aligned nanofibers in the gaps of a metal collector. (B) Analysis of SEM images was performed to estimate the topography of the nanofibers. (C) Aligned nanofibers were collected in the gaps of the collector by tweezers to form yarns. (D) Yarns were functionalized with RGD peptide, cut into 13 mm stripes, and placed inside a 17 mm silicone tube in a way that a 2 mm space was left on either side of the tube. For the control fiber group, the samples were placed in the tube without functionalization. (E) The distribution of fiber diameters (average diameter ᴓ = 112 ± 35 nm) was calculated using NIH ImageJ [27].