Fig. 2.
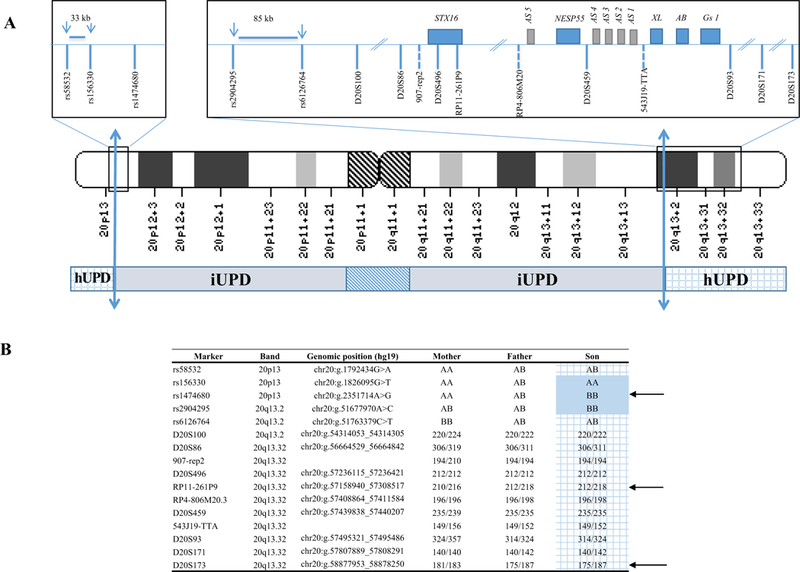
Mixed rearrangement in chromosome 20 (patient 6).
upd(20)pat.arr[GRCh37] 20p13(63244_1792434)x2 htz,20p13q13.2(1800783_51758074)x2 hmz, 20q13.2q13.33(51763379_62909908)x2 htz. A. The inferred breakpoints between paternal isodisomy (iUPD) and paternal heterodisomy (hUPD) are indicated by the two-way arrows: in the short arm, they are located between the last heterozygous SNP (rs58532) (chr20:g.1792434) and the first homozygous one rs156330 (chr20:g.1826095) and in the long arm between rs2904295 (chr20:g.51677970) and rs6126764 (chr20:g.51763379).
B. SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) and microsatellite markers analysis in patient 6 confirmed mixed rearrangement with paternal isodisomy (iUPD) extending from 20p13 to 20q13.2 with telomeric paternal heterodisomy (hUPD)(grid). Arrows indicate informative SNPs or microsatellite markers. The hUPD overlaps the GNAS locus at position 20q13.3.
