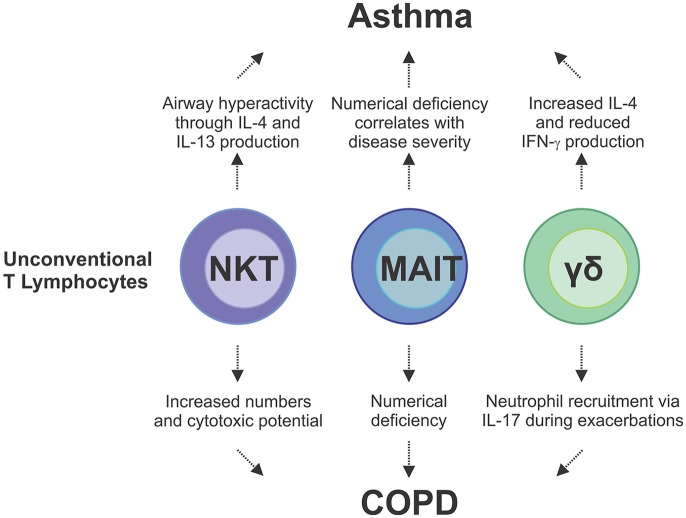
Figure 3.
Unconventional lymphocytes are implicated as pathogenic mediators of asthma and COPD and disease exacerbations. In asthma, IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines produced by NKT cells are directly involved in disease development which is compounded by additional IL-4 production from γδ-T cells. Conversely there is a reduction in IFN-γ producing γδ-T cells and MAIT cells, which correlates with disease severity in asthma and COPD. In COPD, there is an increase in NKT cell numbers and cytotoxicity in the lungs, and IL-17-mediated neutrophilia, which is driven by γδ-T cells, both of which contribute to lung damage. These studies demonstrate the complex interplay and multifaceted contributions from the different types of unconventional T cells to chronic lung disease.