Figure 6.
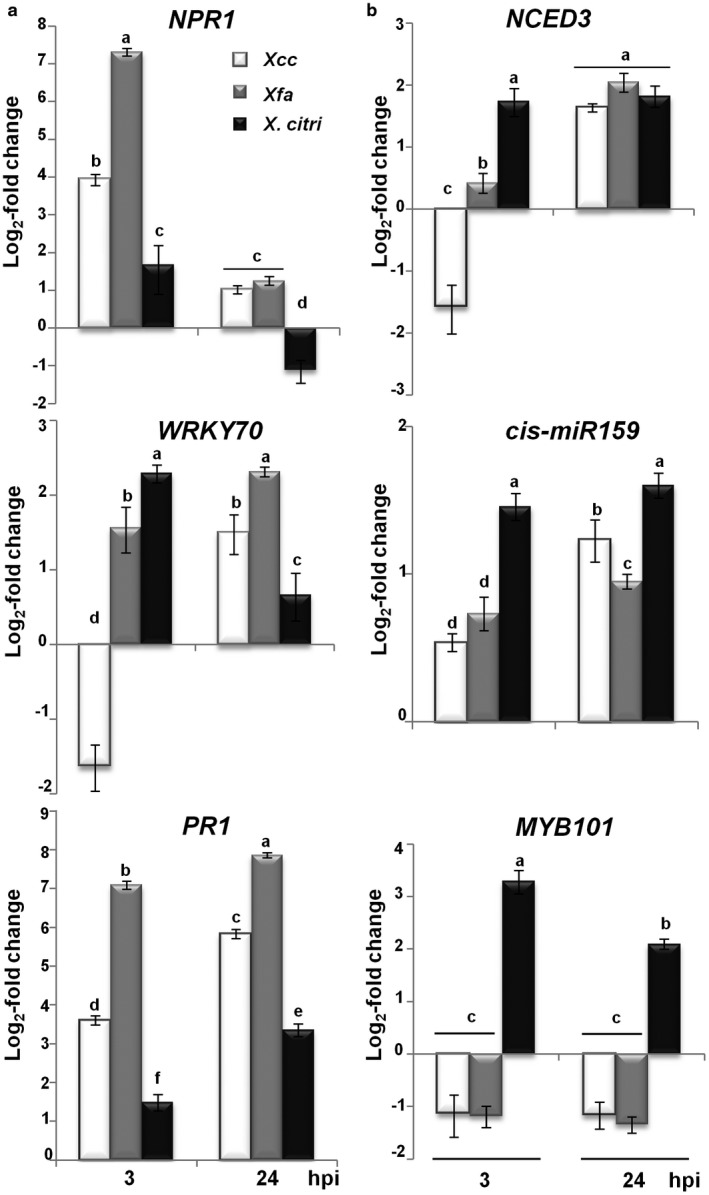
Salicylic acid (SA) signalling pathway is induced, whereas abscisic acid (ABA) synthesis and signalling are repressed, in Citrus limon non‐host resistance (NHR) and the host defence response (HDR). Quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction in leaves inoculated by pressure infiltration with bacterial suspensions [107 colony‐forming units (CFU)/mL] of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc), X. fuscans ssp. aurantifolii (Xfa) strain C and X. citri ssp. citri (X. citri). mRNAs were measured at 3 and 24 h post‐inoculation (hpi). Relative gene expression (ΔΔCt) fold change of mRNA levels was performed considering mock‐treated plants as reference sample and histone H4 transcript as an endogenous control. Values are expressed as means ± standard deviation (SD) from three independent biological replicates. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 [two‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey’s test]. (a) Expression profiles of SA signalling pathway genes encoding non‐expressor of pathogenesis‐related genes 1 (NPR1), WRKY70 transcription factor and pathogenesis‐related 1 (PR1). (b) Expression profiles of ABA biosynthesis (9‐cis‐epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, NCED3) and signalling (MYB101 and csi‐miR159) encoding genes.
