Figure 1.
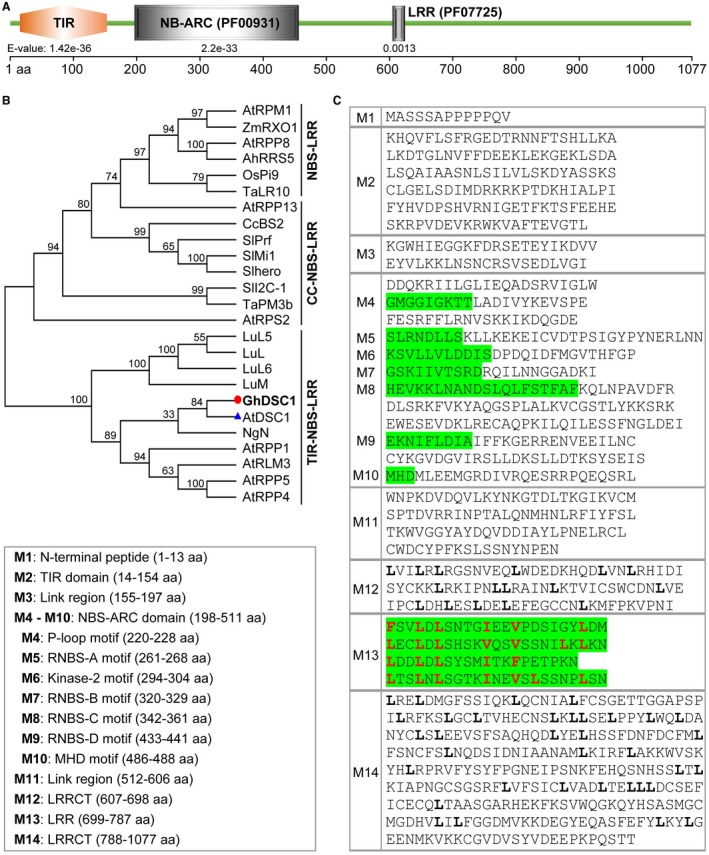
GhDSC1 from Gossypium hirsutum encodes a TIR‐NBS‐LRR protein. (A) Peptide domain prediction in GhDSC1. Conserved domains of GhDSC1 were predicted using the web‐based programme SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/). TIR, Toll ‐ interleukin 1 ‐ resistance; NB‐ARC, nucleotide‐binding adaptor shared APAF‐1, R proteins and CED‐4; LRR, leucine‐rich repeat. E‐value represents the confidence of the predicted domains. (B) Phylogenetic tree constructed using GhDSC1 and known NBS‐LRR resistant proteins. The phylogeny was constructed by Mega 6.0, using maximum‐likelihood (Parameters: 1000 bootstraps, Jones‐Taylor‐Thornton model). GhDSC1 and the closest orthologue DSC1 (named AtDSC1 in this figure) from A. thaliana were labelled with a red dot and blue triangle, respectively. The known NBS‐LRR proteins include A. thaliana AtRPM1 (GeneBank: AGC12590.1), AtRPP13 (GeneBank: AAF42831.1), AtRPP8 (GeneBank: BAC67706.1), AtDSC1 (GeneBank: NP_192938.1), AtRPP1 (GeneBank: NP_190034.2), AtRLM3 (GeneBank: AEE83835.1), AtRPP4 (GeneBank: AAM18462.1), AtRPP5 (GeneBank: AAF08790.1) AtRPS2 (GeneBank: AAM90858.1); Solanum lycopersicum SlPrf (GeneBank: AAF76312.1), SlMi1 (GeneBank: AAC97933.1), SlI2C‐1 (GeneBank: AAB63274.1), Slhero (GeneBank: CAD29728.1); Linum usitatissimum LuL6 (GeneBank: AAA91022.1), LuL (GeneBank: AAD25969.1), LuM (GeneBank: AAB47618.1), LuL5 (GeneBank: AAD25972.1); Nicotiana glutinosa NgN (GeneBank: AAA50763.1); Capsicum chacoense CcBS2 (GeneBank: AAF09256.1); Triticum aestivum TaPM3b (GeneBank: AAQ96158.1), TaLR10 (GeneBank: AAQ01784.1); Zea mays ZmRXO1 (GeneBank: AAX31149.1); Oryza sativa OsPi9 (GeneBank: ABB88855.1); Arac hishypogaea AhRRS5 (Zhang et al., 2017). (C) Analysis of GhDSC1 sequence characteristics. Sequence characteristics were drawn by the multiple sequence alignment of the GhDSC1 to known TIR‐NBS‐LRR proteins. The amino acids represented in green indicate conserved motifs (labelled in M1–M14); search of LRRs (L, M and N regions) was conducted using the web‐based programme LRRfinder (http://www.lrrfinder.com/lrrfinder.php), L and N regions were predicted as LRRCT (PF01463: Leucine‐rich‐repeat C‐terminal domain). The leucine (L) residues were marked in bold font. Four LRRs were predicted and the L residues and similar hydrophobic amino acid residues were marked in red font.
