Figure 1.
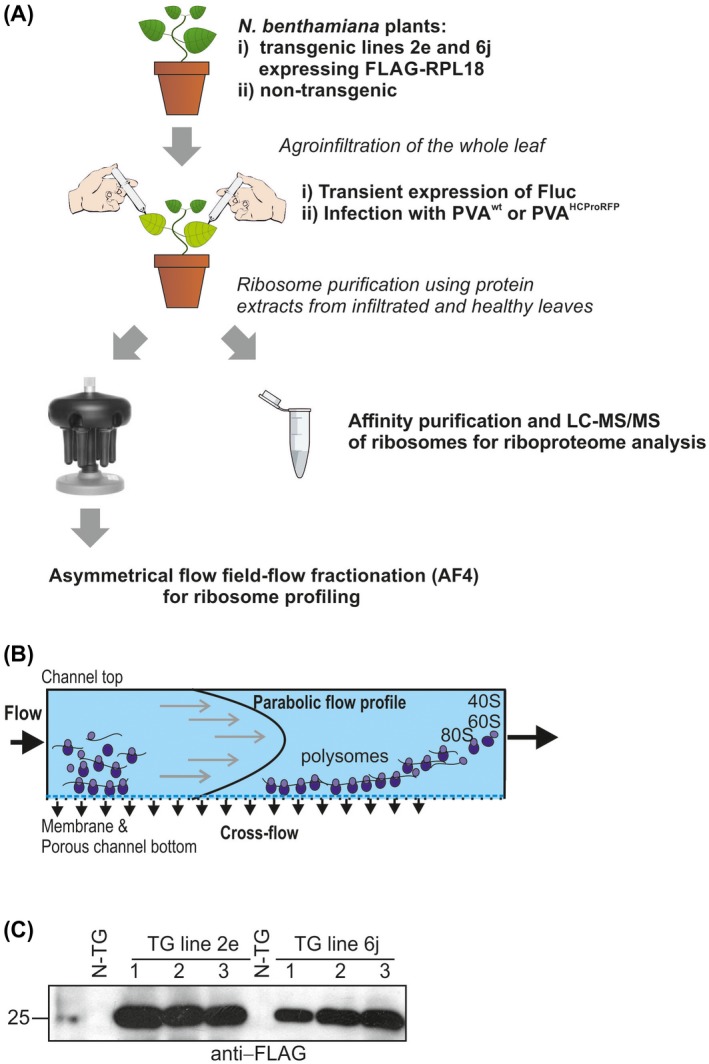
Workflow used in this study. (A) Ribosome purification procedures. Non‐transgenic or transgenic Nicotiana benthamiana plants expressing FLAG‐tagged RPL18 from Arabidopsis thaliana were infected with Potato virus A (PVA) through agroinfiltration (PVA‐infected plants). In addition, plants were agroinfiltrated with firefly luciferase (Fluc) expression construct (Agrobacterium‐infected plants) or were left non‐treated (healthy plants). Infiltrated leaves were collected at 3 and 4 days post‐infection (dpi) and employed to purify the ribosomes using ultracentrifugation or anti‐FLAG immunoaffinity resin. Further separation of ribosomal subunits, monosomes and polysomes for ribosome profiling was achieved by asymmetrical flow field‐flow fractionation (AF4). Affinity‐purified ribosomes were further analysed by liquid chromatography‐tandem mass spectrometry (LC‐MS/MS). (B) The operating principle of AF4. Sample components are separated gently without stationary phase based on their hydrodynamic sizes by the application of two simultaneous flows: channel flow and cross‐flow. In a default elution mode, small sample components elute before the larger ones. (C) Western blot analysis with anti‐FLAG antibodies showing the expression of FLAG‐tagged RPL18 in transgenic N. benthamiana lines 2e and 6j. FLAG‐tagged RPL18 levels were comparable in both transgenic lines. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
