Figure 4.
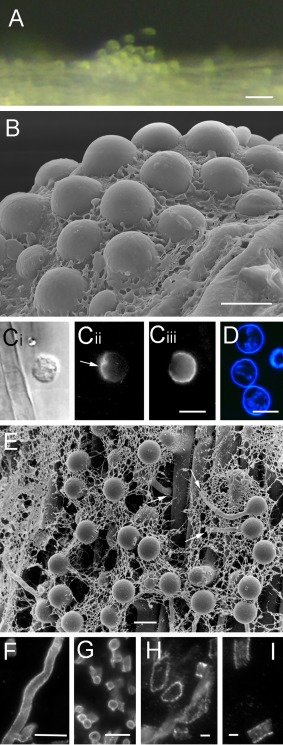
Adhesion and penetration by Phytophthora cinnamomi on the plant surface. (A) Aggregation of motile zoospores on the surface of a plant root. (B) A cluster of cysts embedded in mucin‐like material secreted during encystment on a root surface. (C) A cyst on the surface of a plant root labelled with PcVsv1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) (Cii) or soybean agglutinin (SBA) (Ciii). The same cell is shown in bright field in (Ci). Proteins secreted from zoospore ventral vesicles form an adhesive pad between the cyst and the root (arrow in Cii). SBA binds to N‐acetylgalactosyl and galactosyl residues in PcCpa2 glycoproteins that are secreted from dorsal vesicles onto the zoospore dorsal surface which faces away from the root (Ciii). (D) The cell wall that is rapidly formed on the surface of young cysts is stained by calcofluor. (E) Cysts on the surface of a plant root germinate and the germ tube often penetrates the root along the periclinal wall between adjacent epidermal cells (arrows). (F–I) Secreted cell wall‐degrading enzymes coat the surface of P. cinnamomi hyphae. Polygalacturonases (F–H) and endoglucanases (I) are immunolabelled by polyclonal antibodies raised against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Martel et al., 1996), Fusarium moniliforme (De Lorenzo et al., 1987), Colletotrichum lindemuthianum (Hugouvieux et al., 1995) and Macrophomina phaseolina (Jones and Wang, 1997) enzymes, respectively. Bars: (A) 50 µm; (B–G) 10 µm; (H, I) 2 µm.
