Figure 1.
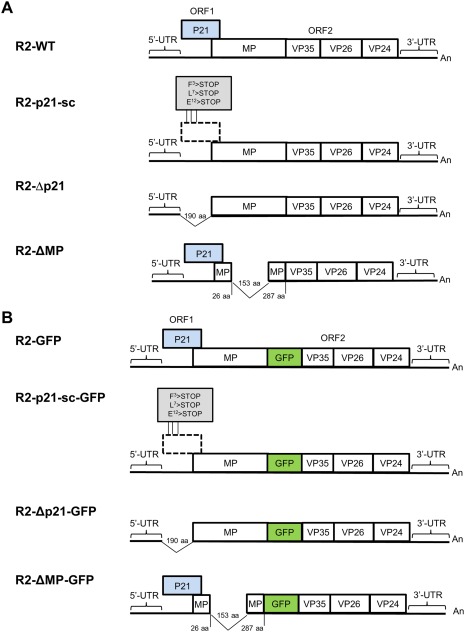
Constructs used in this study. Schematic representation of pJL89‐M‐R2 (R2‐WT, A), pJL89‐M‐R2‐GFP (R2‐GFP, B) (Ferriol et al., 2016a) and the series of RNA2 mutant constructs used in this study (A and B). The RNA genome is depicted with horizontal lines. Boxes indicate open reading frames (ORFs) and the relative positions of regions encoding the RNA2‐ORF1 protein (P21, represented with a blue box), and the regions encompassing a putative movement protein (MP) and the three capsid proteins (VP35, VP26, VP24). The 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) are shown as black lines highlighted by horizontal parentheses. The polyadenylated tail is shown at the 3′ end of the RNA (An). The positions of the stop codons introduced in R2‐p21‐sc and R2‐p21‐sc‐GFP are highlighted in a grey box. Further details of the tomato apex necrosis virus (ToANV) RNA2 deletion mutants are provided in the graphic representation. GFP, green fluorescent protein; aa, amino acid.
