Figure 1.
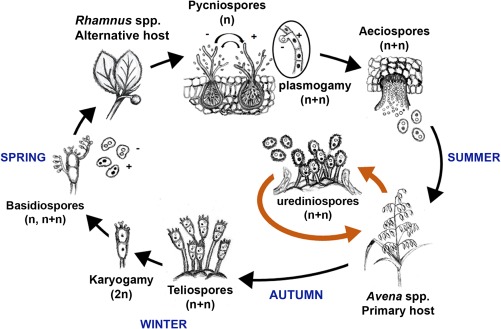
Life cycle of Puccinia coronata f. sp. avenae. The asexual phase of the cycle (orange arrows) is completed in domestic and wild oat species during summer as multiple rounds of infection. The sexual phase of the cycle begins with the differentiation of teliospores in late summer or autumn to withstand cold winter temperatures. Teliospores undergo karyogamy and complete one meiotic event to produce basidiospores in the spring. Basidiospores carry either the (–) or (+) mating type and probably undergo mitosis prior to germination and infection of buckthorn (Rhamnus species). In buckthorn, the fungus differentiates pycniospores, which come into contact with neighbour hyphae from the opposite mating type, enabling plasmogamy. Aeciospores then form and infect oat to re‐initiate the asexual cycle. Drawing by M. Figueroa.
