Figure 6.
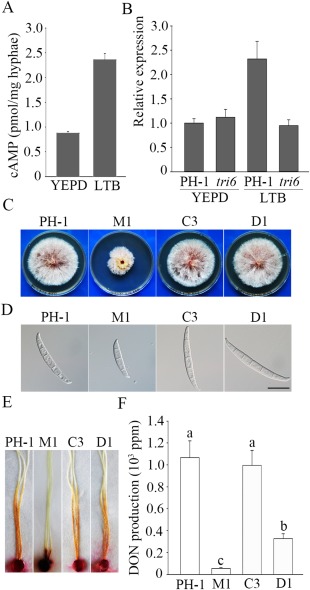
The putative Tri6‐binding site in the FgCAP1 promoter is important for its function during deoxynivalenol (DON) production. (A) The intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) level was assayed using hyphae from the wild‐type strain PH‐1 harvested from 3‐day‐old yeast extract peptone dextrose (YEPD) and LTB (liquid trichothecene biosynthesis) cultures. (B) Expression levels of FgCAP1 in 3‐day‐old YEPD or LTB cultures of PH‐1 and the tri6 mutant. The relative expression level of FgCAP1 in YEPD cultures of PH‐1 was arbitrarily set to unity. Means and standard errors were calculated using results from three independent biological replicates. (C) Three‐day‐old potato dextrose agar (PDA) cultures of PH‐1, Fgcap1 mutant M1 and transformants of M1 expressing the wild‐type FgCAP1 ΔWT (C3) or mutant allele of FgCAP1 ΔTri6B (D1) with deletion of the Tri6‐binding site. (D) Conidia of the same set of strains harvested from 5‐day‐old carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) cultures. Bar, 20 μm. (E) Typical infected corn silks were photographed at 6 days post‐inoculation (dpi). (F) DON production in 7‐day‐old LTB cultures of the same set of strains.
