Figure 8.
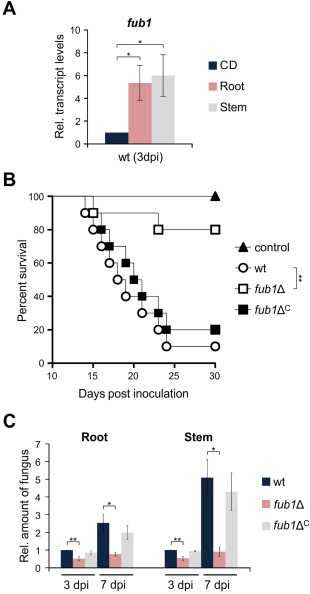
Fusaric acid (FA) production is required for full virulence of Fusarium oxysporum on tomato plants. (A) Quantitative real‐time reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) was performed in the wild‐type strain germinated for 16 h in potato dextrose broth (PDB) and then transferred to Czapek‐Dox liquid (CDL) for 3 h or for inoculated tomato roots and stems at 3 days post‐inoculation (dpi). Transcript levels of fub1 are expressed relative to those in CDL. (B) Groups of 10 tomato plants (cultivar Monika) were inoculated by dipping roots into a suspension of 5 × 106 freshly obtained microconidia/mL of the indicated fungal strains. Percentage survival was plotted for 30 days. Data shown are from one representative experiment. Experiments were performed three times with similar results. (C) Quantitative real‐time PCR was used to measure the relative amount of fungal DNA in total genomic DNA extracted from tomato roots and stems at 3 and 7 dpi with the indicated strains. Amplification levels are expressed relative to those of plants infected with the wild‐type strain. wt, wild‐type strain. Bars represent standard deviations from two independent biological experiments with three technical replicates each.*P < 0.05; **P < 0.001.
