Figure 1.
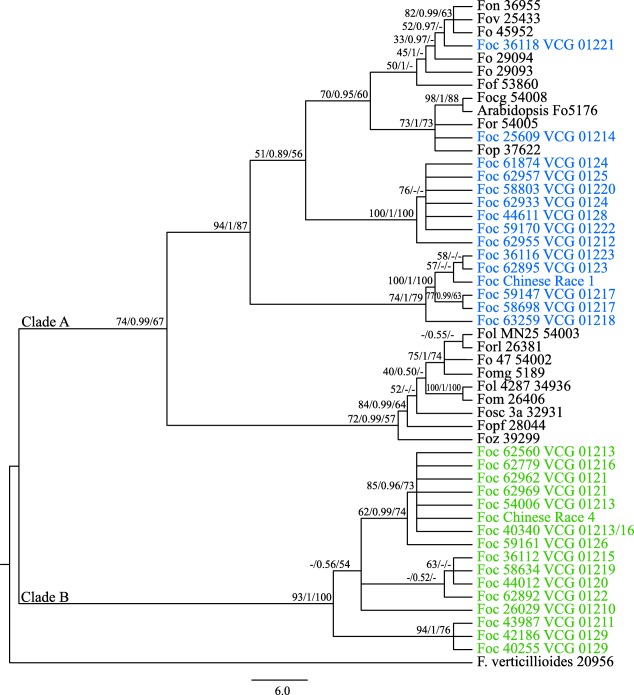
Best infraspecies phylogenetic tree inferred using maximum likelihood (ML) from the concatenated datasets of translation elongation factor‐1α (EF‐1α), RNA polymerase II subunit I (RPB1) and RNA polymerase II subunit II (RPB2) identified in isolates of Fusarium oxysporum used in this study. Trees with similar topologies were also inferred using maximum parsimony (MP) and Bayesian interference (BI) methods. Internal node support is indicated as ML bootstrap proportions/Bayesian probabilities/MP bootstrap proportions. The two major clades are as indicated. For each isolate, the abbreviated forma specialis and accession code as defined in Tables 3 and 4 are indicated. The isolates of F. oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) are also labelled with their respective vegetative compatibility group (VCG). The isolates of Foc in clade A are shown in blue, whereas the isolates of Foc in clade B are shown in green. The other formae speciales and F. verticillioides NRRL 20956 are shown in black. Nucleotide sequences from F. verticillioides served as an outgroup to root the tree.
