Figure 1.
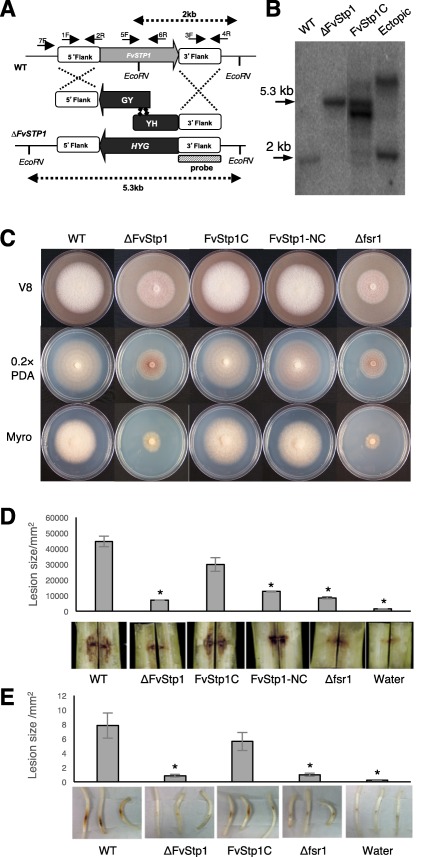
Functional characterization of F. verticillioides STRIP1/2 homolog FvSTP1. (A) Schematic representation of the homologous gene recombination strategy resulting in knockout mutant strain. Hygromycin phosphotransferase (HPH) was used as the selective marker. Arrows indicate primers used for PCR. HYG, hygromycin phosphotransferase gene, HY, HYG 5’ partial amplicon, YG, HYG 3’ partial amplification. (B) Southern analyses of wild‐type (WT), knockout mutant (DFvStp1), complementation (FvStp1C) and ectopic strains. 3’‐flanking region was used as a probe for Southern hybridization. Genomic DNA samples were digested with EcoRV. Anticipated band sizes before and after recombination are indicated above and under the scheme picture. (C) Vegetative growth of WT, DFvStp1, complementation strains (FvStp1C and FvStp1‐NC), and Dfsr1 were examined on V8, 0.2XPDA, and Myro agar plates. Strains were point inoculated with an agar block (0.5 cm in diameter) and incubated for 6 days at 25 °C under 14 h light/10 h dark cycle. (D) Eight‐week‐old B73 maize stalks were inoculated with 108/ml spore suspensions of fungal strains at the internodal region and incubated in a growth chamber for 10 days at 25 °C. Subsequently, maize stalks were split longitudinally to quantify the extent of the rot by Image J software. Three independent biological repetitions were performed. (E) Germinating B73 seedlings were inoculated with 108/ml spore suspension of fungal strains on mesocotyls. Lesion areas were quantified by Image J after 2‐week incubation. Asterisk above the column indicates statistically significant difference (P<0.05) analyzed by t‐Test.
