Figure 5.
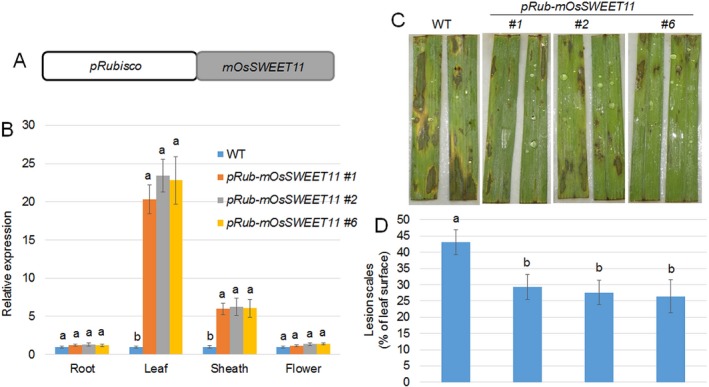
Expression levels of OsSWEET11 and disease symptoms in the transgenic plants expressing mOsSWEET11 under the control of the Rubisco promoter. (A) Schematic diagram showing the construct used for the generation of transgenic plants. The Rubisco promoter was used to drive mOsSWEET11, a mutated form of OsSWEET11. (B) The expression levels of OsSWEET11 were analysed in the roots, leaves, sheaths and flowers of wild‐type and three independent transgenic plants (pRub‐mOsSWEET11 #1, #2 and #6) by quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR). The experiments were repeated three times. Significant differences at P < 0.05 are indicated by different letters. (C) The leaves of wild‐type and three independent transgenic plants (pRub‐mOsSWEET11 #1, #2 and #6) were infected with Rhizoctonia solani AG1‐1A and photographed after 3 days of infection. Six leaves from each line were analysed, and the experiments were repeated three times. (D) The lesion scales were analysed for the R. solani AG1‐1A‐infected leaves shown in (C) by determination of the lesion area on the leaf surface. Data represent means ± standard error (SE) (n > 10). Significant differences at P < 0.05 are indicated by different letters.
