Figure 6.
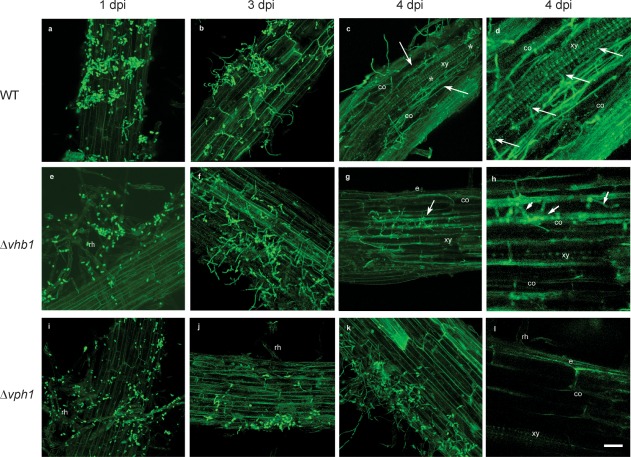
Confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) images of the time course of the colonization process of tomato roots by Verticillium dahliae wild‐type (WT) and mutant green fluorescent protein (GFP)‐tagged strains (in green). Confocal analysis was performed on 3–4‐cm‐long roots to show surface and inner V. dahliae colonization. Images are projections of 25 adjacent confocal optical sections. The focal step between confocal optical sections was 0.5 μm. (a) Surface colonization of tomato roots by WT at 1 day post‐inoculation (dpi). (b) Surface colonization of tomato roots by WT at 3 dpi. Most of the conidia have germinated and proliferation of hyphae can be observed on the root surface. (c, d) Confocal optical sections of internal colonization (arrowed) and intercellular colonization of the vascular tissue (*) by WT at 4 dpi. (e) Surface colonization of tomato roots by Δvhb1 at 1 dpi. Root hairs are externally colonized by Δvhb1 conidia. (f) Surface colonization of tomato roots by Δvhb1 at 3 dpi. Proliferation of hyphae on the root surface is observed. (g, h) Intercellular colonization of the cortical tissue (arrowed) of the tomato root by Δvhb1 at 4 dpi. The vascular tissue was never invaded by Δvhb1. (i) Surface colonization of tomato roots by Δvph1 at 1 dpi. Root hairs are externally colonized by Δvph1 conidia. (j) Surface colonization of tomato roots by Δvph1 at 3 dpi. Only some hyphae were observed on the root surface. (k, l) Superficial colonization of the tomato root by Δvph1 at 4 dpi. The cortical tissue was never invaded by Δvph1. Scale bar represents 20 μm in all panels. co, cortical cells; e, epidermis; rh, root hairs; xy, xylem vessel cells.
