Figure 3.
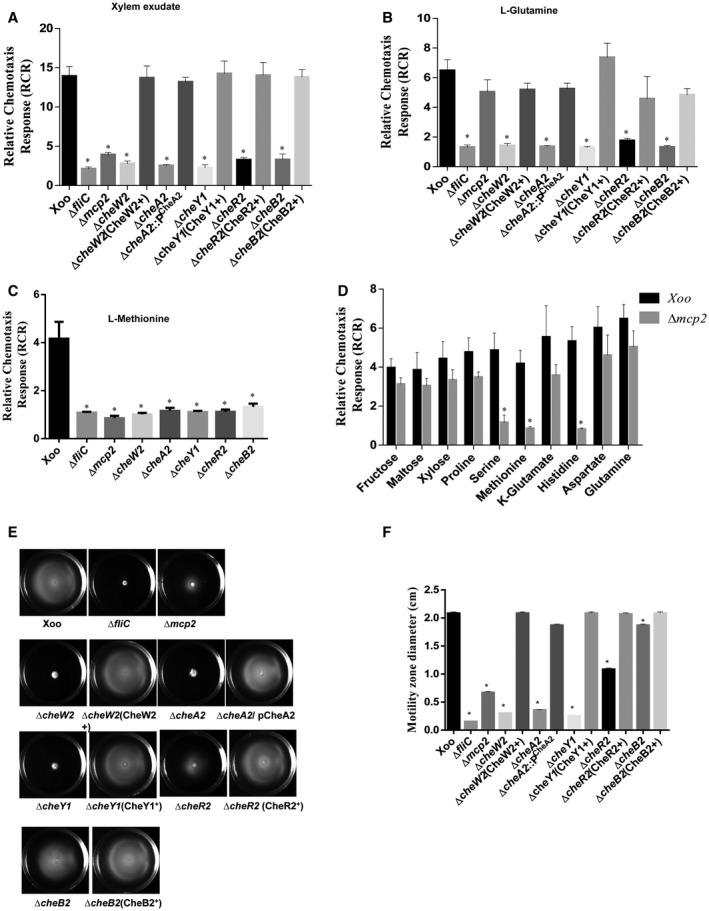
The Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) core chemotaxis components CheW2, CheA2, CheY1, CheR2 and CheB2 are required for the flagellar‐mediated chemotactic response. Quantitative chemotaxis capillary assay with different Xoo strains: Xoo (wild‐type), ΔfliC, Δmcp2, ΔcheW2, ΔcheA2, ΔcheY1, ΔcheB2, cheR2. Cells were incubated at 28 °C with capillaries containing 0.22‐µm filter‐sterilized rice xylem exudate (A), l‐glutamine (B), l‐methionine (C) and phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS). The relative chemotaxis response was determined as the number of migrated bacterial cells in the capillary containing xylem exudate, l‐glutamine or l‐methionine to the number of migrated bacterial cells in the capillary containing PBS. (D) Quantitative chemotaxis assay for the Δmcp2 mutant with different chemoattractants for which the Xoo wild‐type strain exhibited a strong chemotactic response. The relative chemotaxis response was determined as the number of migrated bacterial cells in the test capillary containing chemoattractant to the number of migrated bacterial cells in the capillary containing PBS. Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 6). (E) Swim plate motility assay for different Xoo strains: Xoo (wild‐type), ΔfliC, Δmcp2, ΔcheW2, ΔcheA2, ΔcheY1, ΔcheB2, cheR2 and mutants harbouring the reconstructed wild‐type allele on the chromosome. (F) Motility zone diameter quantification from semisolid swim plate motility assay. Data are shown as the mean ± SD (n = 6). *Statistically significantly different values compared with the wild‐type strain (Student’s t‐test; P < 0.001). The experiment was repeated at least three times.
