Figure 4.
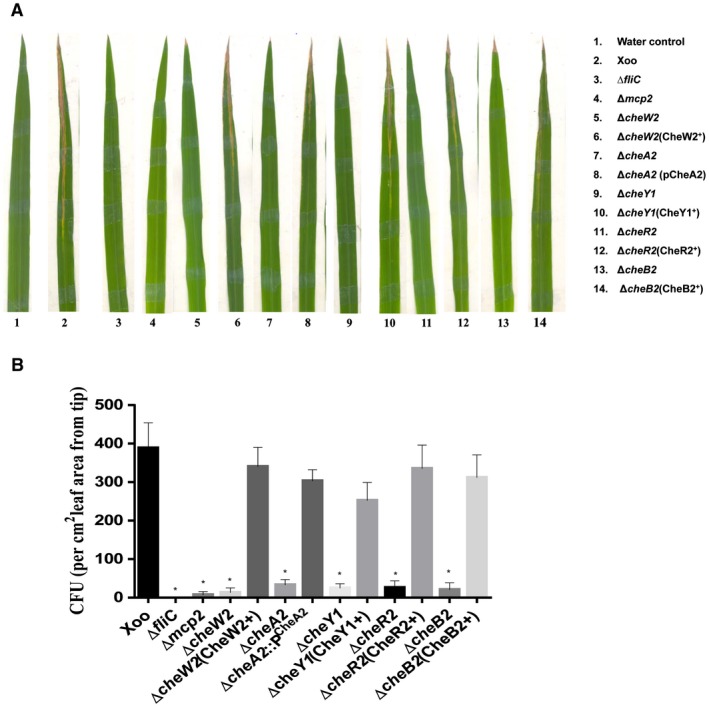
The Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) chemotaxis system is required for the epiphytic (surface) mode of infection and entry into rice leaves. (A) Representative photograph of typical symptoms of bacterial leaf blight (BLB) in the epiphytic mode of infection by different strains of Xoo: Xoo (wild‐type), ΔfliC, Δmcp2, ΔcheW2, ΔcheA2, ΔcheY1, ΔcheB2, cheR2. The fresh, healthy rice leaves with intact tips of 30‐day‐old susceptible rice plants (TN‐1) were either dipped in water (control) alone or in bacterial suspension. Lesion lengths and percentage efficiency of infection were measured at 21 days post‐inoculation. (B) Leaf entry assay by epiphytic mode of infection. Inoculations were performed by dipping 12–15‐day‐old leaves of rice seedlings in bacterial cultures for 1 min. Leaves were then washed and surface sterilized to remove bacteria attached to the leaf surface, homogenized and dilution plated to determine the number of colony‐forming units (CFU) per cm2 of leaf area from the tip, representative of bacterial cells inside the leaf. Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 5). *Statistically significantly different values compared with the wild‐type strain (Student’s t‐test; *P < 0.001). The experiment was repeated at least three times. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
