Figure 4.
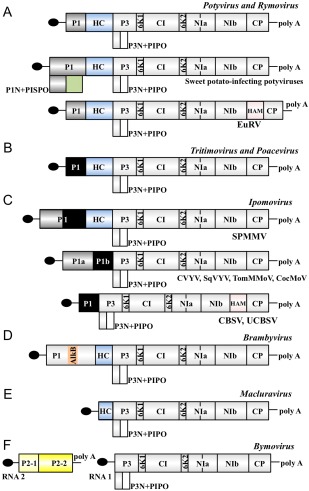
Schematic representation of genomic organization in viruses from different genera of the family Potyviridae. The long open reading frame is shown as a box divided into mature viral products. PIPO open reading frame is indicated as the box below P3. The terminal protein VPg is depicted as a black ellipse. P1a and P1a‐like proteins are represented by grey boxes, whereas P1b and P1b‐like proteins are represented by black boxes. Features that are not shared by all potyvirids are highlighted in different colours. (A) Potyvirus and Rymovirus genera. The PISPO open reading frame in sweet potato‐infecting potyviruses is indicated as a pale green box below P1. The extra protein HAM between NIb and CP in Euphorbia ringspot virus (Knierim et al., 2017) is highlighted in pink. (B) Tritimovirus and Poacevirus. (C) Ipomovirus. The diversity among members of this genus has been reviewed (Dombrovsky et al., 2014). A HAM extra protein (in pink) was also present in a subset of ipomoviruses. (D) Brambyvirus. The AlkB domain in P1 from Blackberry virus Y is highlighted in pale orange. (E) Macluravirus. (F) Bymovirus. RNA2, unique in the Potyviridae family, is highlighted in yellow.
