Figure 3.
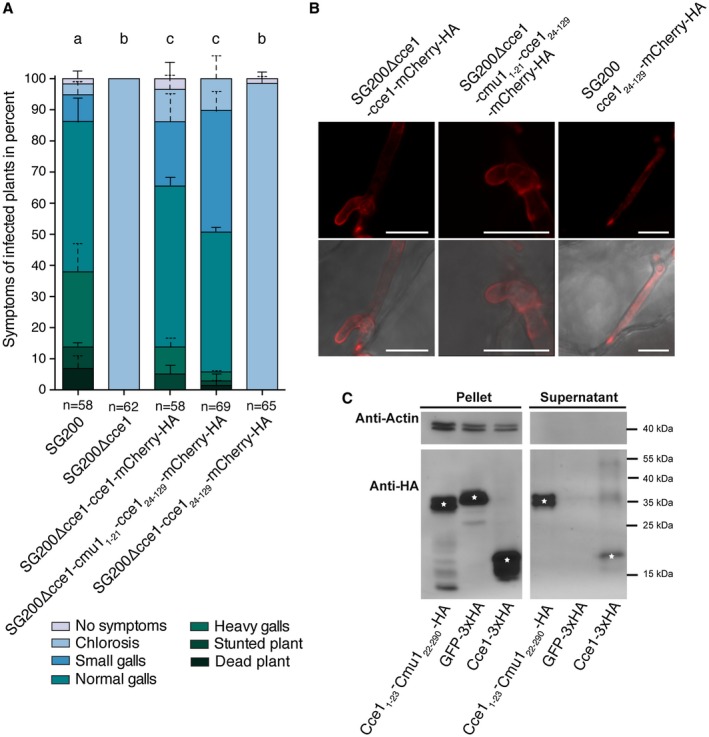
Disease symptom rating and secretion of Cce1. (A) Seven‐day‐old Z. mays seedlings were infected with the U. maydis strains SG200, SG200Δcce1, and the three complementation strains SG200Δcce1‐cce1‐mCherry‐HA, SG200Δcce1‐cmu11‐21‐cce124‐129‐mCherry‐HA, and SG200Δcce1‐cce124‐129‐mCherry‐HA. Disease symptoms were scored twelve days post infection (dpi). Mean and standard deviation of relative counts from two replicates are displayed. For clarity, only positive error bars are shown. n = number of plants scored. Significant differences between the strains are indicated by a, b, c. p‐values calculated by Fisher’s exact test, MTC by Benjamini‐Hochberg algorithm. α = 0.05 (B) Localization of Cce1‐mCherry‐HA fusion proteins with and without secretion signal. The Cce1‐mCherry‐HA fusion proteins containing endogenous Cce1 signal peptide (left) as well as the same construct containing the signal peptide from Cmu1 (middle) are localized mainly at the periphery of the fungus. The Cce1‐mCherry‐HA version without secretion signal (right) is located in the cytoplasm of the fungus. Photomicrographs were taken seven days post infection. Upper row: mCherry fluorescence (red); lower row: overlay of mCherry channel and brightfield. Scale bar = 10 μm. (C) Secretion of Cce1 in axenic culture. Cce1‐3xHA protein as well as Cce11‐23‐Cmu122‐290‐HA was detected by immunoblotting in the pellet as well as in the supernatant of the strain AB33 Potef‐cce1‐3xHA and AB33 Potef‐cce11‐23‐cmu122‐290‐HA, respectively, whereas cytosolic GFP‐3xHA as well as actin was only detected in the cell pellet fraction. White asterisks on the immunoblot bands indicate the expected band size for the respective immunolabelled proteins.
