Figure 3.
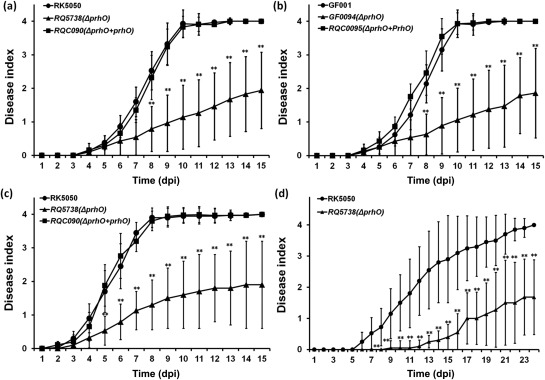
Pathogenicity test. Ralstonia solanacearum strains used: (a, c, d) OE1‐1 derivatives; (b) GMI1000 derivatives. Test plants: (a, b, c) tomato plants; (d) tobacco plants. Inoculation methods: (a, b) soil‐soaking inoculation; a bacterial suspension was poured into the soil of plants at a final concentration of 107 colony‐forming units (cfu)/g of soil; (c) petiole inoculation; about 3 μL of bacterial suspension at 108 cfu/mL was dropped onto the freshly cut petiole surface; (d) leaf infiltration in tobacco leaves; about 50 μL of bacterial suspension at 108 cfu/mL was infiltrated into tobacco leaves with a blunt‐end syringe. Filled circles, wild‐type strains; filled triangles, prhO mutants; filled squares, prhO mutants complemented with OE1‐1 prhO. Plants were inspected daily for wilting symptoms and scored on a disease index scale of 0–4 (0, no wilting; 1, 1%–25% wilting; 2, 26%–50% wilting; 3, 51%–75% wilting; 4, 76%–100% wilting or death). dpi, days post‐inoculation. Each assay was repeated in four independent trials and each trial contained at least 12 plants. Mean values of all results were averaged and are presented with standard deviation (SD) (error bars). Significance level: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (t‐test).
