Figure 2.
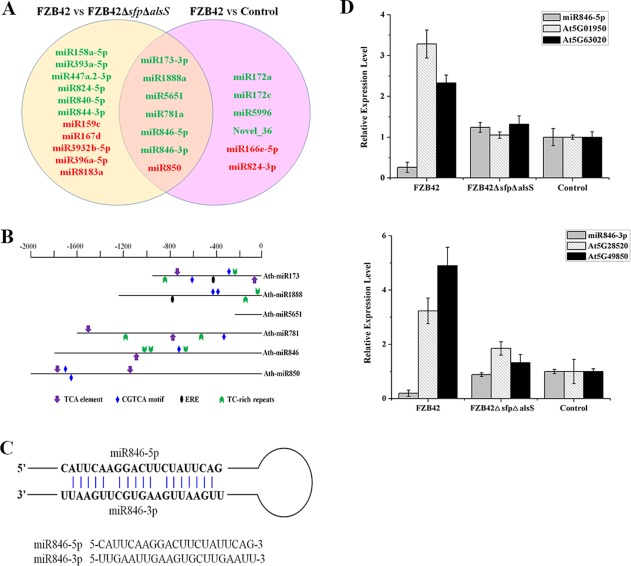
miR846‐5p and miR846‐3p are induced systemic resistance (ISR)‐associated microRNAs (miRNAs) after inoculation with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. (A) Venn diagram of differentially expressed miRNAs between FZB42 and FZB42ΔsfpΔalsS and FZB42 and control. Red represents up‐regulated miRNAs and green represents down‐regulated miRNAs. (B) Cis‐elements in the promoter regions of differentially expressed miRNAs. The defence‐responsive cis‐elements distributed on the sense strand and reverse strand are shown above and below the black lines, respectively. TCA, CGTCA and ERE elements represent cis‐acting elements involved in salicylic acid, jasmonic acid and ethylene responsiveness, respectively. TC‐rich repeat represents cis‐acting element involved in defence responsiveness. (C) Secondary stem‐loop structure for miR846‐5p and miR846‐3p with mature miRNA sequences indicated. (D) Expression levels of miR846‐5p, miR846‐3p and their target genes (At5G01950 and At5G63020 for miR846‐5p; At5G49850 and At5G28520 for miR846‐3p) from Arabidopsis leaves after inoculation with B. amyloliquefaciens FZB42, FZB42ΔsfpΔalsS and control. Data are expressed as the relative expression of the respective mRNAs normalized to the endogenous actin 2. The experiment was repeated three times. Error bars represent significant differences according to Fisher's least‐significant difference test (P = 0.05) using SPSS software.
