Figure 3.
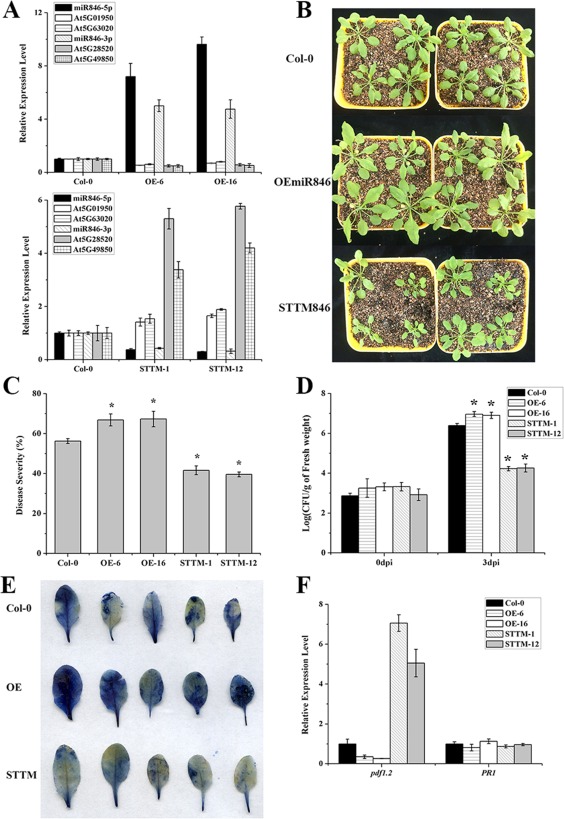
The miR846 expression level in Arabidopsis is negatively correlated with disease resistance. (A) Expression levels of miR846‐5p/miR846‐3p and their target genes were detected in transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing miR846‐5p/miR846‐3p (OEmiR846) or with knockdown of miR846‐5p/miR846‐3p (STTM846) by stem‐loop quantitative reverse transcription‐polymerase chain reaction (qRT‐PCR). The leucine‐rich repeat genes (AT5G01950 and AT5G63020) were predicted as the targets of miR846‐5p. The jacalin lectin genes (At5G49850 and At5G28520) were predicted as the targets for miR846‐3p. (B) Phenotypes of transgenic Arabidopsis OEmiR846 and STTM846. Photographs were taken 4 weeks after germination. (C) Disease severity of transgenic Arabidopsis OEmiR846 and STTM846 after Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pst DC3000) infection for 7 days. *Highly significant difference (P < 0.05). (D) Quantification of Pst DC3000 growth in transgenic Arabidopsis OEmiR846 and STTM846. *Highly significant difference (P < 0.05). CFU, colony‐forming unit; dpi, days post‐inoculation. (E) Cell death in transgenic Arabidopsis OEmiR846 and STTM846 leaves after Pst DC3000 infection for 7 days. Blue areas represent cell death. (F) Expression levels of disease resistance‐associated genes in transgenic Arabidopsis OEmiR846 and STTM846 were detected by qRT‐PCR. Pathogenesis‐related protein (PR1) and plant defence factor 1.2 (PDF 1.2) represent marker genes involved in the salicylic acid‐ and jasmonic acid‐dependent defence signalling pathways in Arabidopsis. Error bars represent significant differences according to Fisher's least‐significant difference test (P = 0.05) using SPSS software. Each experiment was repeated three times.
