Figure 4.
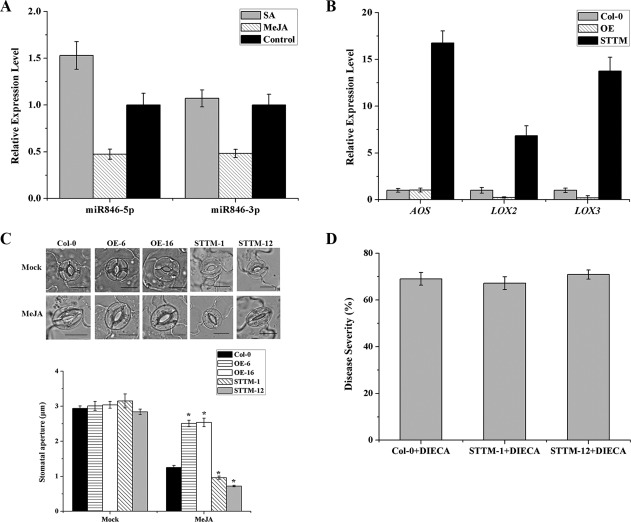
miR846 modulates induced systemic resistance in Arabidopsis through the jasmonic acid (JA)‐dependent signalling pathway. (A) Expression levels of miR846‐5p/miR846‐3p were detected in wild Arabidopsis Col‐0 after spraying with 1 mm salicylic acid (SA) or 0.1 mm methyl jasmonate (MeJA). (B) Expression levels of JA biosynthesis genes (AOS, LOX2 and LOX3) in transgenic Arabidopsis OEmiR846 and STTM846. (C) Stomatal apertures in transgenic Arabidopsis OEmiR846 and STTM846 after the addition of 0.1 mm MeJA. Scale bars indicate 10 μm. Values represent the means of 50 random selected stomata. (D) Disease resistance of STTM846 against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (Pst DC3000) after spraying with the JA biosynthetic inhibitor diethyldiethiocarbamic acid (DIECA). Four‐week‐old STTM846 transgenic Arabidopsis and wild‐type Col‐0 were previously sprayed with 200 μm DIECA containing 0.02% (v/v) Tween‐20. Twenty‐four hours later, DIECA‐treated plants were inoculated with 108 colony‐forming units (CFU)/mL Pst DC3000. Disease severity was determined according to the disease index measured at 7 days post‐inoculation (dpi). Each treatment had 12 plants and the experiment was repeated three times. Error bars represent significant differences according to Fisher's least‐significant difference test (P = 0.05) using SPSS software. *Highly significant difference (P < 0.05). All experiments were repeated three times.
