Figure 10.
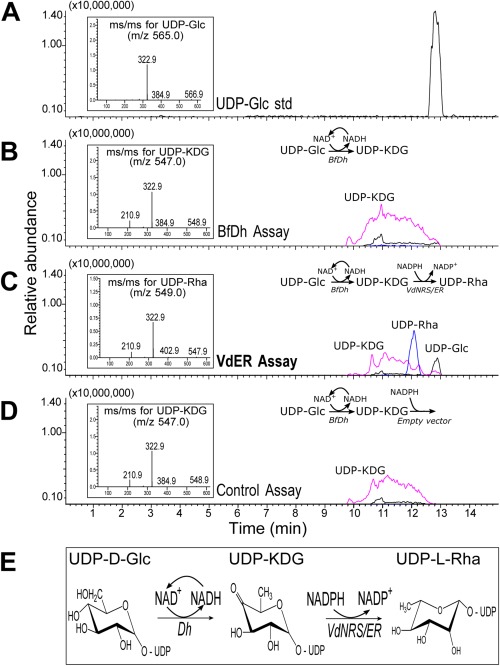
VdNRS/ER (NRS/ER, nucleotide‐rhamnose synthase/epimerase‐reductase) converts uridine diphosphate‐4‐keto‐6‐deoxy‐glucose (UDP‐KDG) to UDP‐rhamnose. (A) UDP‐glucose (UDP‐Glc) standard elutes from a HILIC (hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography) column at 12.8 min and is detected by mass spectrometry (MS) with m/z 565 [M – H]–. The MS/MS of the parent ion (inset) gives m/z 323 and 385 diagnostic ion fragments, [UMP – H]– and [UDP – H2O – H]–, respectively. (B) HILIC separation of products from the enzymatic reaction with BfDh (4,6‐dehydratase) displays a peak with the same retention time as UDP‐KDG with diagnostic [M – H]– m/z 547 and MS/MS ion fragment with m/z 323. (C) HILIC separation of products from the dual enzymatic reaction with BfDh and VdNRS/ER displays a peak with the same retention time as UDP‐rhamnose (UDP‐Rha) with diagnostic [M – H]– m/z 549 and MS/MS of 403, 323, 210. (D) Dual enzymatic reaction with BfDh and an empty vector control displays a peak with the same retention time as UDP‐KDG with diagnostic [M – H]– m/z 547 and MS/MS ion fragment with m/z 323. (E) UDP‐rhamnose metabolic pathway in fungi showing the enzymes involved in the sequential conversion of UDP‐Glc to UDP‐Rha.
