Figure 4.
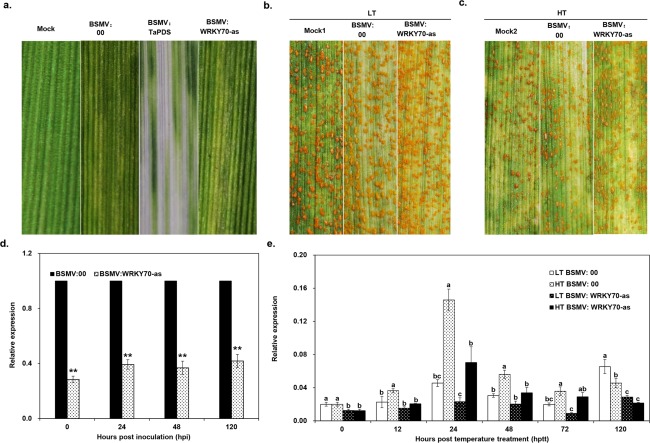
Functional analyses of TaWRKY70 during high‐temperature seedling plant (HTSP) resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst) using a Barley stripe mosaic virus (BSMV)‐induced gene silencing (VIGS) system. (a) Mild chlorotic mosaic symptoms of BSMV at 9 days post‐inoculation (dpi) (mock, plants treated with FES buffer). Disease symptoms on the fourth leaves pre‐inoculated with BSMV‐derived RNAs, challenged with Pst race CYR32 and then subjected to low‐temperature (LT, 15 ºC) (b) and high‐temperature (HT, 20 ºC) (c) treatments. 0 h post‐temperature treatment (hptt), 192 h post‐inoculation (hpi) from which HT was applied; disease symptoms were photographed at 14 dpi. Mock1 and Mock2, wheat plants were pre‐inoculated with FES, and then inoculated with CYR32 and subjected to LT and HT treatments, respectively. (d) Efficiency of silencing of TaWRKY70 by VIGS under LT treatment after Pst inoculation. **Student's t‐test (P < 0.01) indicates significant differences in the mean TaWRKY70 expression level between the BSMV:WRKY70‐as‐inoculated plants and BSMV:00‐inoculated plants. (e) Induction of TaWRKY70 in the fourth leaves pre‐inoculated with BSMV:00 or BSMV:TaWRKY70‐as under HT or LT treatments. The error bars represent standard errors. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted and followed by Duncan's multiple range test (P = 0.01); the means of the TaWRKY70 expression level do not differ significantly if they contain at least one common lowercase letter.
