Figure 4.
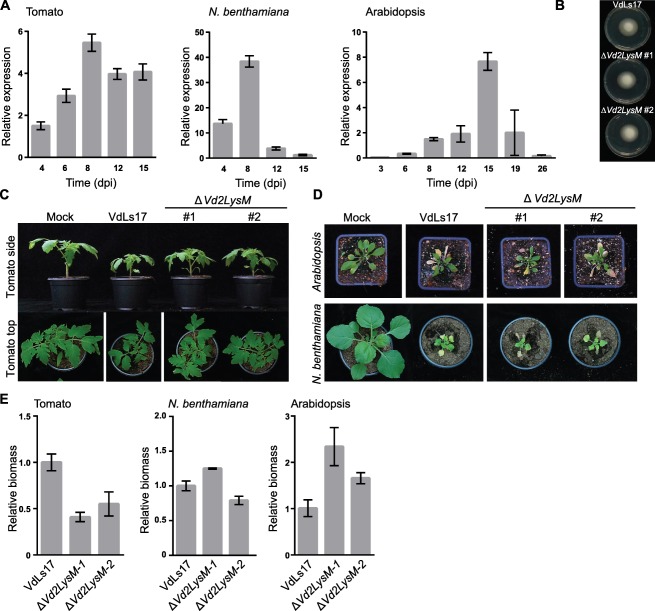
Lineage‐specific LysM effector Vd2LysM contributes to the virulence of Verticillium dahliae strain VdLs17 on tomato. (A) Vd2LysM expression during colonization of V. dahliae strain VdLs17 on tomato, N. benthamiana and Arabidopsis plants at 2–26 days post‐inoculation (dpi). (B) Morphology of wild‐type V. dahliae strain VdLs17 and two Vd2LysM deletion strains after 7 days of incubation on potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium at room temperature. (C) Photographs of representative tomato plants out of eight plants that were either mock‐inoculated or inoculated with wild‐type V. dahliae strain VdLs17 or two deletion strains of Vd2LysM at 14 dpi. The infection assay was repeated three times with similar results. (D) Photographs of representative N. benthamiana and Arabidopsis plants out of eight plants that were either mock‐inoculated or inoculated with wild‐type V. dahliae strain VdLs17 or two deletion strains of Vd2LysM at 14 dpi (N. benthamiana) and 21 dpi (Arabidopsis). The assay was repeated three times with similar results. (E) Fungal biomass accumulation in tomato, N. benthamiana and Arabidopsis plants inoculated with wild‐type strain VdLs17 or Vd2LysM deletion strains at 14 dpi (tomato, N. benthamiana) and 21 dpi (Arabidopsis). Error bars represent the standard error of three replicate experiments.
