Figure 1.
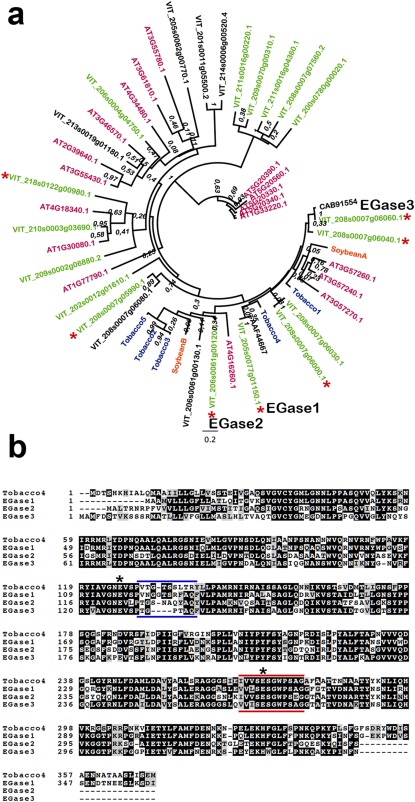
Analysis of grapevine endo‐β‐1,3‐glucanase (EGase) sequences. (a) Phylogenetic tree containing grapevine (black and green), Arabidopsis (magenta), tobacco (blue) and soybean (orange) endoglucanases. Grapevine sequences in green indicate proteins with a predicted signal peptide. Asterisks indicate grapevine genes for which evidence of expression is available. Numbers on the nodes indicate bootstrap values. Sequences selected as EGase1, EGase2 and EGase3 are specified. Grapevine and Arabidopsis endoglucanases are named according to the Grapevine Genome Database (v2) at CRIBI and The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR), respectively (see Experimental procedures). The accession numbers in the tree correspond to the two original sequences used in the blast search. Accession numbers for tobacco and soybean glucanases are as follows: Tobacco1, CAA38324; Tobacco2, AAA34079; Tobacco3, AAD33880; Tobacco4, AAA34078; Tobacco5, AAA34103.1; SoybeanA, AAA33946; SoybeanB, AAR26001. (b) Alignment of the three selected grapevine endoglucanases and a tobacco endoglucanase possessing a vacuolar targeting signal. The black background shows identical amino acid residues. The grey background represents similar amino acids. Asterisks indicate predicted catalytic glutamic acid (Glu) residues. Blue bars show the divergent region in the vicinity of a catalytic Glu. Red bars show the glycosyl hydrolase family 17 signature.
