Figure 1.
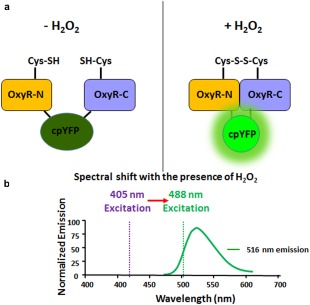
Mechanism of detection of H2O2 with MoHyPer. (a) Domain structure of MoHyPer. In the presence of H2O2, a disulfide bond is formed between two cysteine (Cys) residues located in the amino (N) and carboxyl (C) domains of HyPer. The conformational change drives a ratiometric fluorescence change in circularly permuted yellow fluorescent protein (cpYFP). (b) Spectral shift from 420 nm excitation to 500 nm excitation with the presence of H2O2. Diagram modified from http://genomics.unl.edu/RBC_EDU/hp.html.
