Figure 1.
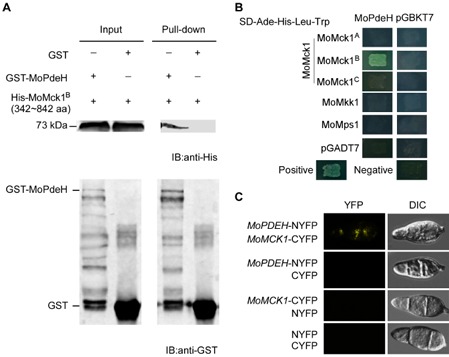
MoPdeH interacts with MoMck1. (A) In vitro pull‐down assay of His‐MoMck1 [342–842 amino acids (aa)] and GST‐MoPdeH. MoMck1A represents the protein of 1–341 aa of the whole‐length protein of MoMck1 (1529 aa for full length), MoMck1B represents 342–842 aa and MoMck1C represents 842–1489 aa of the protein. Recombinant GST‐MoPdeH or GST bound to glutathione Sepharose beads was incubated with E scherichia coli cell lysate containing His‐MoMck1B (342–842 aa). Eluted protein was analysed by immunoblot (IB) with monoclonal anti‐His and monoclonal anti‐GST antibodies. GST, glutathione transferase; His, histidine. (B) Yeast two‐hybrid analysis of the interaction between MoMck1 and MoPdeH. MoPdeH was inserted into vector pGBKT7 and three truncated parts of MoMck1 (MoMck1A, MoMck1B, MoMck1C) were inserted into pGADT7. Yeast cells were grown on synthetic dextrose (SD) medium lacking leucine (Leu), tryptophan (Trp), His and adenine (Ade), and β‐galactosidase (LacZ) activities were investigated with positive and negative controls. Plates were incubated at 30 °C for 3 days before being photographed. (C) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for the interaction between MoMck1 and MoPdeH. Conidia of transformants expressing the MoPDEH‐NYFP and MoMCK 1‐CYFP constructs were tested by both differential interference contrast (DIC) and epifluorescence microscopy. YFP, yellow fluorescent protein.
