Figure 1.
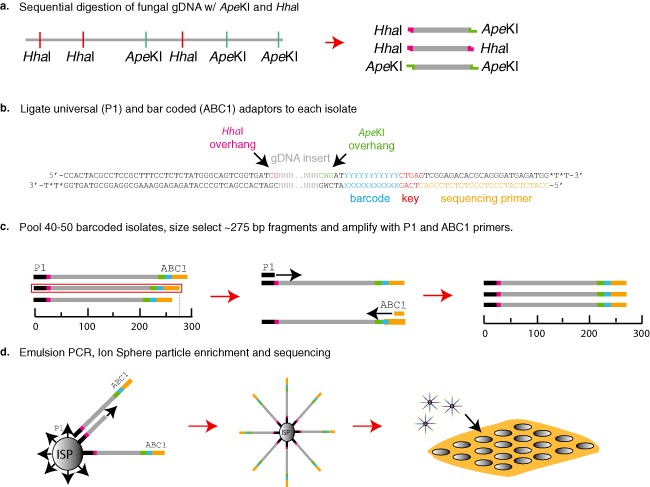
Genotype‐by‐sequencing (GBS) protocol for fungal genomes. (a) Fungal genomic DNA was sequentially digested with the restriction enzymes HhaI then ApeKI, producing three different combinations of restriction termini. (b) The ABC1 adaptor containing the sequencing primer site (orange), Ion Torrent key site (red), barcodes (blue) and ApeKI sticky ends (green), and the P1 adaptor containing the Ion Sphere Particle attachment nucleotides (black) and HhaI sticky ends (pink), were ligated to the restriction‐digested genomic DNA fragment. (c) The barcoded fragments were pooled, unligated adaptors were removed and fragments were size selected for ∼275‐bp fragments. The 275‐bp fraction from the pooled libraries was amplified using the Ion Torrent sequencing primers and Ion Sphere Particle (ISP) primer, without sphere particles attached. (d) The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products were quantified and emulsion PCR was performed to add monoclonal DNA templates to a single ISP. The ISPs with DNA templates were enriched on the Ion One Touch 2 bead enrichment station and loaded into single wells on the 318 chip and sequenced on the Ion Torrent PGM™.
