Figure 4.
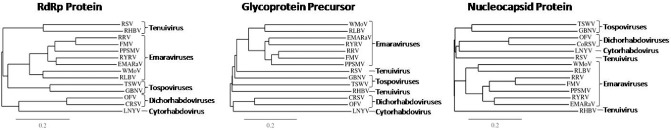
Phylogenetic trees drawn with predicted amino acid sequences of RNA‐1 (RNA‐dependent RNA polymerase), RNA‐2 (glycoprotein precursor) and RNA‐3 (nucleocapsid) of Pigeonpea sterility mosaic virus (PPSMV), together with orthologues of members of the genera Emaravirus, Tenuivirus, Cytorhabdovirus, Dichorrhabdovirus and Tospovirus. All the sequences of the polypeptides were retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database and the multiple sequence alignments were performed using the MUSCLE (MUltiple Sequence Comparison by Log‐Expectation) program; the phylograms were drawn using the TreeDyn program. TSWV (Tomato spotted wilt virus, Acc. No. L20953) and GBNV (Groundnut bud necrosis virus, Acc. No. NC003619) are tospoviruses; RSV (Rice stripe virus, Acc. No. JQ927420) and RHBV (Rice hoja blanca virus, Acc. No. AF004658) are tenuiviruses; CoRSV (Coffee ringspot virus, Acc. No. KF812525) and OFV (Orchid fleck virus, Acc. No. AB244417) are dichorhabdoviruses (unassigned negative‐sense, single‐stranded RNA viruses that were previously proposed to be included in the family Rhabdoviridae); LNYV (Lettuce necrotic yellow virus, Acc. No. L30103) is used as an outgroup and is a member of the genus Cytorhabdovirus (family Rhabdoviridae). EMARaV, European mountain ash ringspot‐associated virus; FMV, Fig mosaic virus; RLBV, Raspberry leaf blotch virus; RRV, Rose rosette virus; RYRV, Redbud yellow ringspot virus; WMoV, Wheat mosaic virus.
