Figure 5.
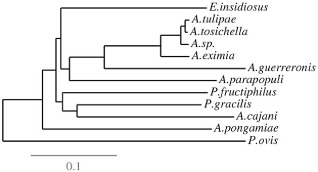
Phylogenetic tree for the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences of the eriophyid mites. The ITS sequences of ∼300–400 nucleotides, corresponding to the pigeonpea mite Aceria cajani (Acc. No. AJ251693), were used to draw the phylogenetic analysis, and the sequences were retrieved from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database. The ITS sequences used are A. cajani (AJ251693), A. eximia (JF920113), A. guerreronis (KJ461967; host plant, coconut), A. parapopuli (JF792237; host plant, poplar), A. pongamiae (AJ251696; host plant, pongamia), Aceria sp. (JQ512784; host plants, sweetpotato and Eastern redbud), A. tosichella (JF960158; host plant, wheat), A. tulipae (AJ251695; host plant, tulip), Eriophyes insidiosus (AJ251694; host plant, peach), Phyllocoptes fructiphilus (AJ251692; host plant, rose), P. gracilis (AJ251697; host plant, raspberry) and Psoroptes ovis (AF270823; hosts: sheep, cattle, goats, horses, rabbits and camelids). Psoroptes ovis, an animal mite (Arthropod; family: Psoroptidae) which causes the contagious sheep scab, was used as an outgroup. Multiple sequence alignments were performed using the MUSCLE (MUltiple Sequence Comparison by Log‐Expectation) program, and the phylograms were drawn using the TreeDyn program.
