Figure 1.
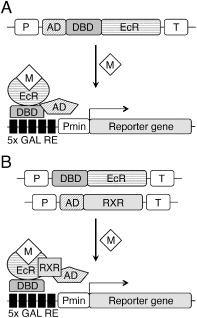
Methoxyfenozide‐inducible expression systems. (A) Monopartite system. This employs a transcription factor comprising a herpes simplex virus‐derived VP16 activation domain (AD), the DNA‐binding domain from Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 (DBD) and an ecdysone receptor domain from Christoneura fumiferana (EcR), which are expressed from a promoter (P) and terminator (T). After binding methoxyfenozide (M), the chimeric transcription factor translocates into the nucleus, where it binds GAL4 response elements (5x GAL4 RE) upstream of a minimal promoter (Pmin) to activate a reporter gene. (B) Bipartite or two‐hybrid system. An active transcription factor results when methoxyfenozide binds to a DBD‐EcR chimera, which binds a chimera of AD and the retinoid X‐receptor from Locusta migratoria (RXR).
