Figure 5.
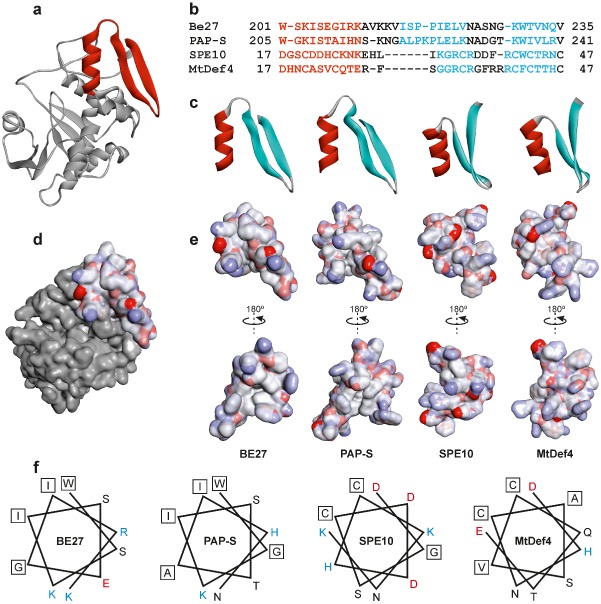
Structure of the α‐helix/γ‐core motif of BE27 compared with PAP‐S (pokeweed antiviral protein) and the defensins SPE10 and MtDef4. (a) Structure of BE27 indicating the position of the α‐helix/γ‐core motif from amino acid 201 to amino acid 235 (red ribbon). (b) Sequence alignments based on the three‐dimensional alignments using the program Expresso (Di Tommaso et al., 2011). Colouring of the alignments indicates the presence of α‐helix (red) or β‐sheet (cyan) secondary structures. (c) Ribbon representation of the α‐helix/γ‐core motif from BE27 expanding from amino acid 201 to amino acid 235 and their homologues from PAP‐S, SPE10 and MtDef4. The α‐helix and β‐strands are coloured in red and cyan, respectively. (d, e) Electrostatic surface of the α‐helix/γ‐core motif from BE27 localized in the whole protein (d) or compared with the same motif in PAP‐S, SPE10 and MtDef4 (e). Electrostatic potential is indicated in red (negative charge), white (neutral) and blue (positive charge). (f) Helical wheel drawing of the helices of BE27, PAP‐S, SPE10 and MtDef4. The amino acid charge is indicated in red (negative), black (neutral) and blue (positive). Hydrophobic amino acids are boxed.
