Figure 3.
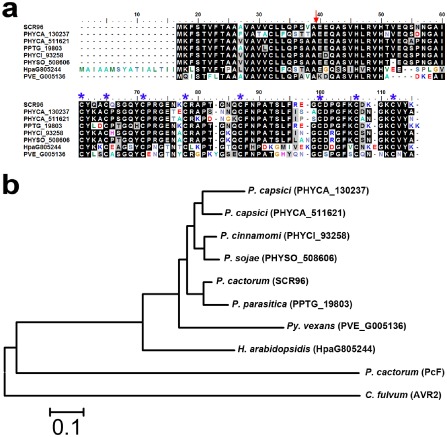
Protein sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis of P hytophthora cactorum SCR96 and its homologues in different oomycete species. (a) Protein sequences were aligned and shaded for consensus (50% threshold for shading) using BioEdit. The homologues of SCR96 compared here include PHYCA_130237 and PHYCA_511621 from P . capsici, PPTG_19803 from P . parasitica, PHYCI_93258 from P . cinnamomi, PHYSO_508606 from P . sojae, HpaG805244 from H yaloperonospora arabidopsidis and PVE_G005136 from P ythium vexans. The predicted cleavage site for signal peptides is indicated by a red arrow. The conserved cysteine sites are marked at the top by blue asterisks for visualization. (b) Phylogeny of SCR96 and homologues from different species. The tree was constructed by the neighbour‐joining (NJ) algorithm implemented in MEGA 5 with 1000 bootstrap replicates. The IDs, except for SCR96, PcF and AVR2, in parentheses after the species names are from the FungiDB database. C ladosporium fulvum AVR2 served as an outgroup in the NJ tree.
